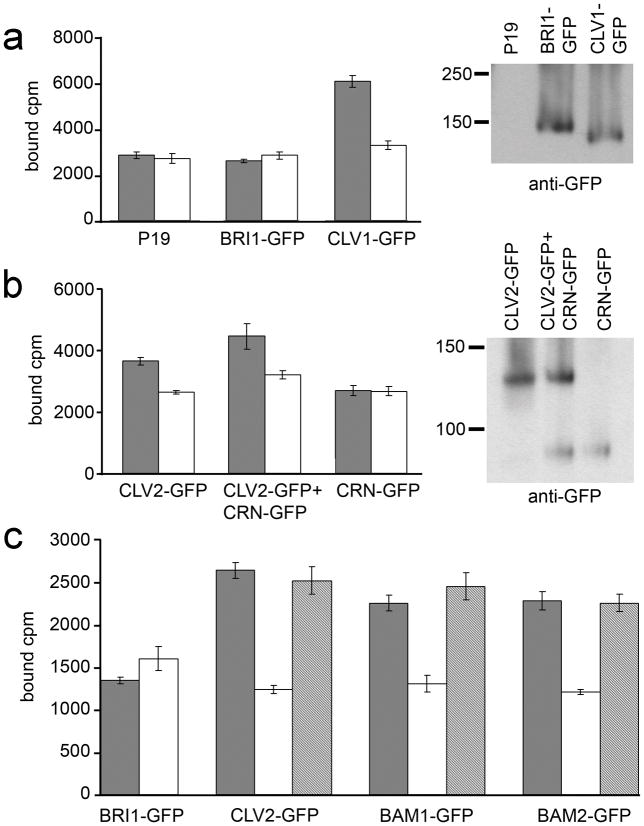
Figure 4. CLV3 CLE binding activity.
(a) Detergent-washed membrane fractions from P19, BRI1-GFP and CLV1-GFP inoculations were tested for 125I-labelled CLV3 CLE peptide binding without (black bars) and with (white bars) excess unlabelled CLV3 CLE competitor. Mean ± standard error over four replicates are shown. The fractions tested for CLE binding were assayed in a protein gel blot with anti-GFP antibodies to detect BRI1-GFP and CLV1-GFP accumulation.
(b) Assays identical to those in (a) performed for CLV2-GFP and CRN-GFP in independent and co-inoculations.
(c) GFP-fused CLV2, BRI1, BAM1 and BAM2 were immunoprecipitated with anti-GFP antibodies and then tested for CLV3 CLE binding activity without (black bars) and with excess unlabelled CLV3 CLE (white bars) or the non-functional CLV3S peptide (grey bars) as competitors. Mean ± standard error over three replicates are shown.