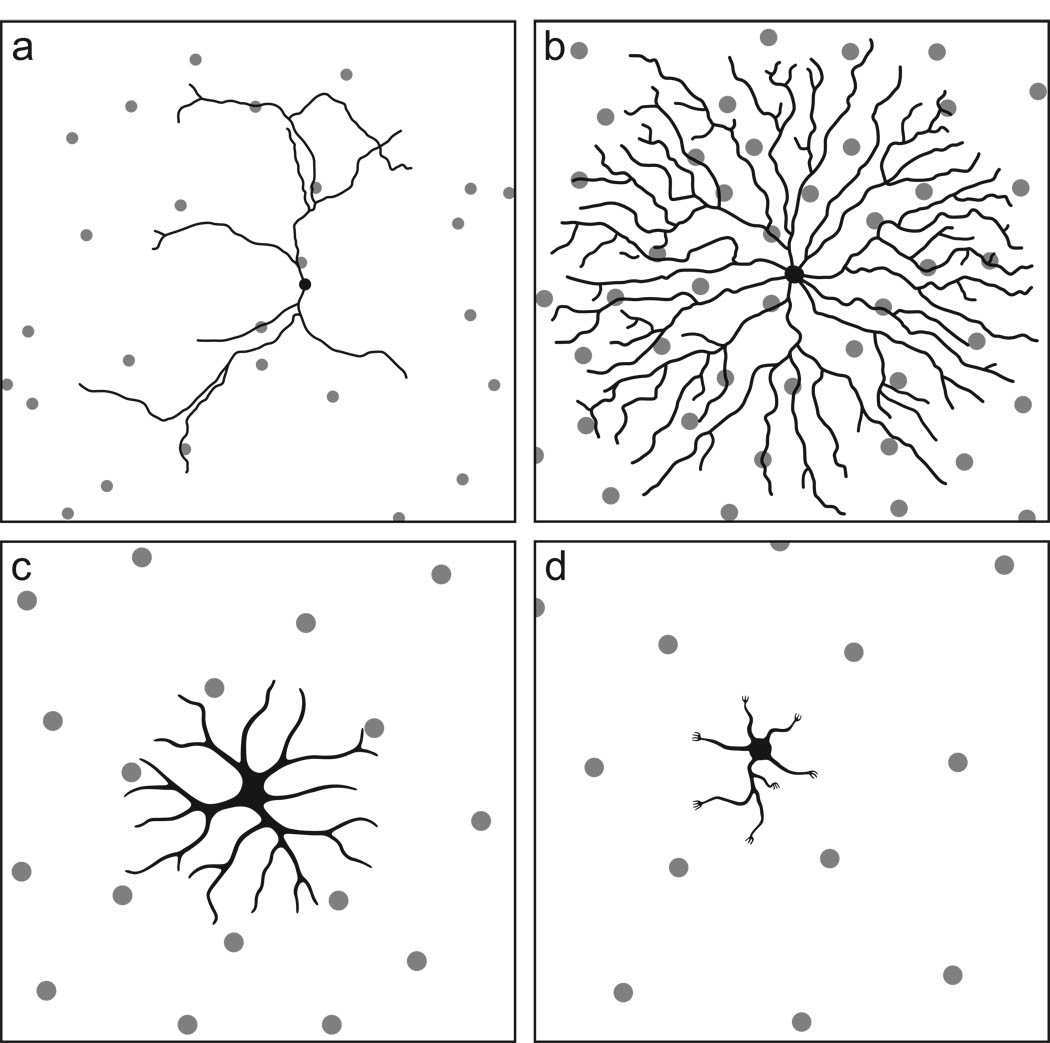
Figure 4.
The morphology of four different retinal cell types in relation to their retinal mosaics. a. Dopaminergic amacrine cells differentiate a dendritic arbor that is indifferent to the presence of other dendrites arising from the same cell as well as from those of homotypic neighbors. b. Cholinergic amacrine cells differentiate a dendritic arbor in which dendrites avoid one another, yet overlaps those of numerous homotypic neighbors. c. Horizontal cell somata constrain further dendritic outgrowth from their homotypic neighbors. d. Bipolar cell dendritic arbors achieve a tiling of the retinal surface, colonizing pedicles within their dendritic fields while also sharing those at the dendritic boundary with adjacent cells. The panels are not drawn to the same scale, intending only to portray the relationship between morphology and homotypic density. (Modified from Reese, 2008b).