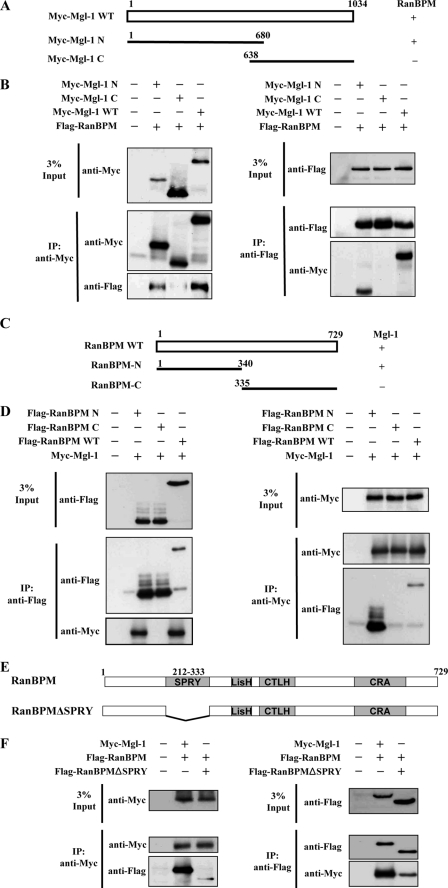
FIGURE 3.
Determination of binding region between Mgl-1 and RanBPM. A, RanBPM interacts with the N terminus of Mgl-1. Schematic structure of Mgl-1 deletion constructs. Wild-type Mgl-1 (WT), Mgl-1 deletion constructs Mgl-1-N1-(1–680), Mgl-1-C-(638–1034) were used to analyze the region of Mgl-1 that interacts with RanBPM. B, 293T cells were co-transfected with FLAG-RanBPM WT, Myc-Mgl-1 WT, and Mgl-1 deletion constructs Myc-Mgl-1-N1-(1–680), and Myc-Mgl-1-C-(638–1034). Immunoprecipitation was performed with either an anti-Myc or an anti-Flag antibody, followed by Western blotting with anti-Myc and anti-Flag antibodies. C, Mgl-1 interacts with the N terminus of RanBPM. Schematic structure of RanBPM deletion constructs. Wild-type RanBPM, RanBPM deletion mutants RanBPM-N-(1–340), RanBPM-C-(335–729) were used to examine the region of RanBPM that interacts with Mgl-1. D, 293T cells were co-transfected with Myc-Mgl-1 WT and FLAG-RanBPM WT and RanBPM deletion constructs FLAG-RanBPM-N-(1–340), and FLAG-RanBPM-C-(335–729). Immunoprecipitation was performed by either an anti-Myc or an anti-Flag antibody, followed by Western blotting with anti-Myc and anti-Flag antibodies. E, Mgl-1 interacts both with RanBPM and RanBPMΔSPRY. Schematic structure of SPRY domain deletion construct of RanBPM (Δaa 212–333). F, 293T cells were transfected with Myc-Mgl-1 WT and Flag-RanBPM WT or Flag-RanBPMΔSPRY. Immunoprecipitation was performed by either an anti-Myc or an anti-Flag antibody and immunoblotted with anti-Flag and anti-Myc antibodies.