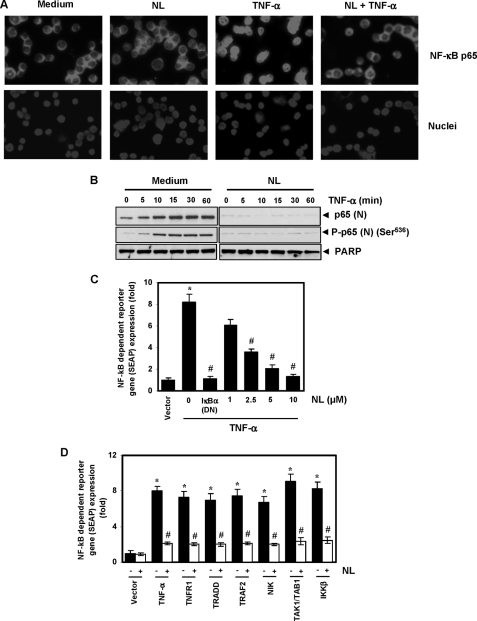
FIGURE 6.
Nimbolide inhibits TNF-α-induced phosphorylation and nuclear translocation of p65 and NF-κB-dependent reporter gene expression induced by TNF-α and different molecules in the NF-κB-signaling pathway. A, immunocytochemical analysis of p65 localization. KBM-5 cells were treated with 10 μm nimbolide for 4 h, exposed to 0.1 nm TNF-α for 15 min, and analyzed for p65 localization. B, KBM-5 cells were untreated or pretreated with 10 μm nimbolide for 4 h and then treated with 0.1 nm TNF-α for the indicated times. Nuclear extracts were prepared and analyzed by Western blotting using antibodies against p65 and phospho-p65 (Ser536). PARP was used as an internal control. Figures are representative of one of three independent experiments. C, nimbolide inhibits TNF-α-induced NF-κB-dependent SEAP expression. A293 cells were transiently transfected with an NF-κB-containing plasmid linked with the SEAP gene. Cells were treated with nimbolide for 4 h at the indicated concentrations, followed by 1 nm TNF-α for 24 h. Cell supernatants were collected and assayed for SEAP activity. The results are expressed as the change in activity relative to the vector control. DN, dominant negative. D, nimbolide inhibits NF-κB-dependent reporter gene expression induced by TNF-α, TNFR1, TRADD, TRAF2, NIK, TAK1/TAB1, and IKK-β. A293 cells were transfected with pNF-κB-SEAP plasmid, expression plasmid, and control plasmid for 24 h and treated with nimbolide. The cell supernatants were then assayed for SEAP activity. Where indicated, the cells were exposed to 1 nm TNF-α for 12 h. The results are expressed as the change in activity relative to the vector control. Values given are the mean ± S.D. of three independent replicates. * and # indicate the significance of difference compared with control and TNF-α/plasmid alone group respectively; p < 0.05. NL, nimbolide.