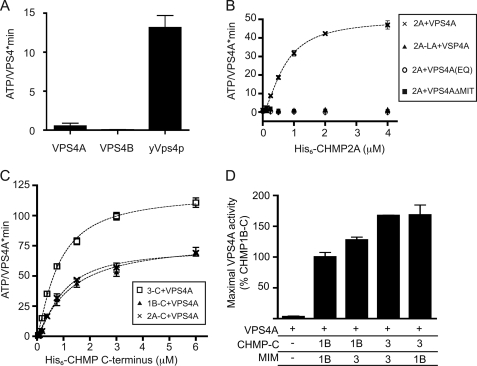
FIGURE 1.
Effect of ESCRT-III proteins that contain MIM1 motifs on VPS4A activity. A, ATP hydrolysis by human VPS4A, VPS4B, and yeast Vps4p assessed under standard reaction conditions of 0.2 μm enzyme and 1 mm ATP at 37 °C. B, effect of CHMP2A on ATP hydrolysis by VPS4A. ×, wild-type VPS4A with varying concentration of wild-type CHMP2A (Vmax 50 ATP/VPS4A·min); triangles, wild-type VPS4A and CHMP2A L216A/L219A; circles, VPS4A E228Q mutant with wild-type CHMP2A; boxes, VPS4AΔMIT mutant with CHMP2A. C, effect of C-terminal CHMP fragments on ATP hydrolysis by VPS4A. Boxes, CHMP3-C (amino acids 115–222), Vmax of 118 ATP/VPS4A·min; ×, CHMP2A-C (amino acids 117–222), Vmax of 72 ATP/VPS4A·min; triangles, CHMP1B-C (amino acids 106–199) with Vmax of 78 ATP/VPS4A·min. D, effect of chimeric CHMP-MIM proteins on ATP hydrolysis by VPS4A. Shown is the activity of VPS4A in response to 6 μm of the indicated protein, scaled to the activity reached with CHMP1B-C (100%). The activity promoted by CHMP1B-C differs compared with CHMP1B-3 (p = 0.046), as does the activity promoted by CHMP3-C versus CHMP1B-3 (p = 0.0067); the activity promoted by CHMP3-C is not significantly different from that of CHMP3–1B. Error bars indicate S.D. from one experiment conducted in duplicate or triplicate; all experiments were repeated three times.