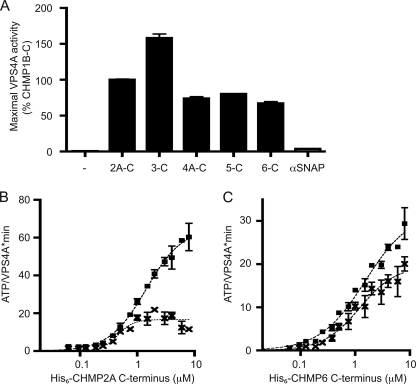
FIGURE 2.
All six subclasses of ESCRT-III proteins stimulate VPS4A ATPase activity. A, maximal ATP hydrolysis by VPS4A in the presence of C-terminal fragments of CHMP1B(106–199), CHMP2A(117–222), CHMP3(115–222), CHMP4A(119–222), CHMP5(121–219), CHMP6(118–201), or α-SNAP. Assays were conducted as described in the legend to Fig. 1C; maximal activity for each protein was scaled to a CHMP1B-C control present on each assay plate. B, effect of mutating the MIM1 motif in CHMP2A-C. Squares, ATP hydrolysis by VPS4A in the presence of wild-type CHMP2A-C. ×, ATP hydrolysis by VPS4A in the presence of MIM1 mutant CHMP2A-L216A/L219A. C, effect of mutating the MIM2 motif in CHMP6-C. Squares, ATP hydrolysis by VPS4A in the presence of wild-type CHMP6-C. ×, ATP hydrolysis by VPS4A in the presence of MIM2 mutant CHMP6-L170D,V173D. Error bars indicate S.D. from duplicate reactions of one experiment; all experiments were repeated three times.