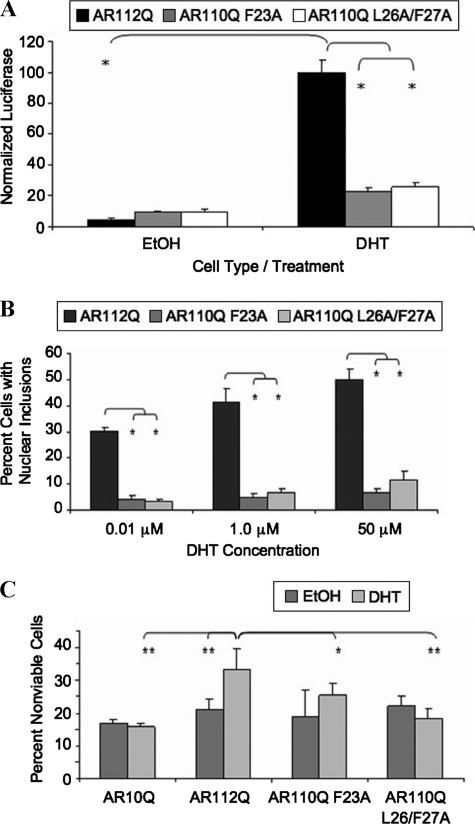
FIGURE 6.
Mutation of the FXXLF motif of AR polyQ-expanded AR prevents the N/C interaction, nuclear inclusions, and toxicity in an SBMA cell model. A, mammalian two-hybrid assay was performed as described in the legend for Fig. 5, including the AR111Q-F23A or ARQ111-L26A/F27A mutant fused to a VP16 activation domain. Student's t test was performed (*, p < 0.01). B, stably transfected PC12 cells were induced to express equivalent levels of AR10Q, AR112Q, AR110Q-F23A, or AR110Q-L26A/F27A. Cells were treated with increasing amounts of DHT (0.01, 1.0, and 50 μm) for 48 h, fixed, and immunostained as in Fig. 1A. Over 1000 cells were counted, and the percentage of cells containing nuclear inclusions graphed. Student's t test was performed (*, p < 0.02). C, toxicity was assessed as in Fig. 2A. Two-way ANOVA was performed (**, p < 0.001;*, p < 0.01). The findings are representative of three independent experiments.