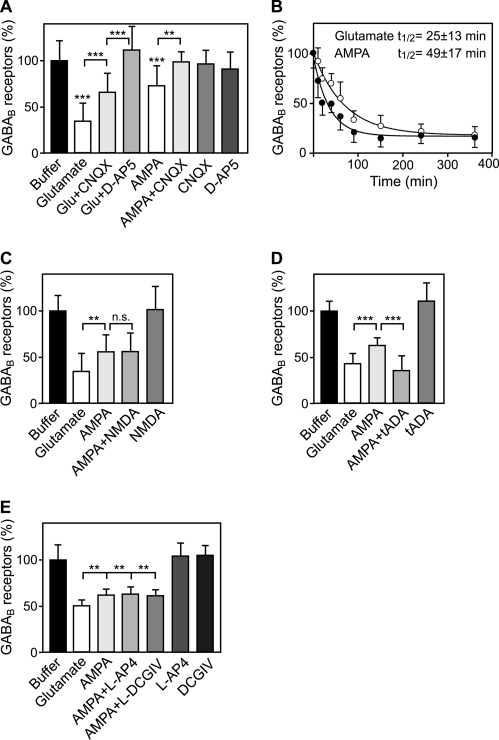
FIGURE 2.
Glutamate-induced down-regulation of GABAB receptors is mediated by AMPA receptors and accelerated by type I mGluRs. A, glutamate-induced down-regulation of GABAB receptors is partially reversed by the AMPA antagonist 6-cyano-7-nitroquinoxaline-2,3-dione (CNQX) and fully reversed by the NMDA antagonist D-AP5. Cells were treated for 90 min either with 50 μm glutamate, 100 μm AMPA, 20 μm 6-cyano-7-nitroquinoxaline-2,3-dione, 50 μm D-AP5, or with the indicated combinations and tested for GABAB receptor levels using the in-cell Western assay, and antibodies, which were directed against the C terminus of GABAB1. Means ± S.D.; n = 27–44 cultures from three to five preparations; **, p < 0.01; ***, p < 0.001, one-way ANOVA; Bonferoni post test. B, selective activation of AMPA receptors mimics the effect of glutamate but is less efficient in down-regulating GABAB receptors. Neurons were incubated with 50 μm glutamate or 100 μm AMPA and were analyzed for GABAB receptor levels at different time points (10 min to 6 h) using the in-cell Western assay. Data were fitted to one-phase exponential decay: glutamate, t½ = 25 ± 13 min; AMPA, t½ = 49 ± 17 min. Mean ± S.D.; n = 12 cultures from three preparations. C–E, combined activation of AMPA and mGluR group I receptors (D), but not AMPA and NMDA (C) or mGluR group II or III receptors (E), mimic glutamate-induced down-regulation of GABAB receptors. Neurons were incubated for 90 min with either 50 μm glutamate, 100 μm AMPA, 100 μm NMDA + 10 μm glycine, 200 μm tADA (mGluR1/5 agonist), 100 μm L-AP4 (mGluR4/6/7/8 agonist), or 100 μm (2S,1R,2R,3R)-2-(2,3-dicarboxycyclopropyl)glycine (DCGIV) (mGluR2/3 agonist) alone or with the indicated combinations. Means ± S.D.; C, n = 24 cultures from three preparations; D, n = 21 cultures from three preparations; E, n = 32 cultures from four preparations. n.s. = p > 0.05, **, p < 0.01; ***, p < 0.001, one-way ANOVA; Bonferoni post test (C and D) or Dunnett's post test (E).