FIGURE 4.
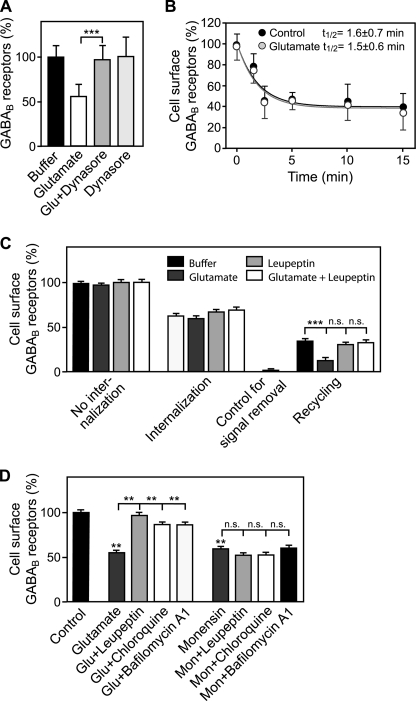
Glutamate affects recycling but not internalization of GABAB receptors. A, inhibition of dynamin with Dynasore completely blocks the glutamate-induced down-regulation of GABAB receptors. Neurons were treated either with 50 μm glutamate, 100 μm Dynasore, or with 50 μm glutamate + 100 μm Dynasore for 90 min and subjected to the in-cell Western assay for determination of GABAB receptor levels. Means ± S.D., n = 40 cultures from five preparations; ***, p < 0.001, one-way ANOVA; Bonferoni post test. B, glutamate did not affect the rate of GABAB receptor internalization. Cell surface receptors of neurons were labeled at 4 °C for 60 min with F(ab′)2 fragments of an antibody directed against the N terminus of GABAB2. Neurons were then incubated for 1.5–15 min at 37 °C in the presence or absence of 50 μm glutamate followed by determination of cell surface GABAB receptor levels. Mean ± S.D.; glutamate: n = 18 cultures, three preparations; AMPA: n = 12 cultures, two preparations. C, glutamate reduces recycling of internalized receptors back to the cell surface. Cell-surface receptors of neurons were labeled as described above, and neurons were incubated for 15 min at 37 °C in the presence or absence of 50 μm glutamate, 100 μm leupeptin, or 50 μm glutamate + 100 μm leupeptin to allow internalization of receptors. After masking remaining antibody-tagged cell-surface receptors with secondary antibodies not detected by the imaging system, neurons were incubated again for 30 min at 37 °C to allow internalized receptors to recycle back to the plasma membrane. Recycled receptors were detected using an appropriately labeled secondary antibody for 90 min at 4 °C. Means ± S.E., n = 30–94 cultures from four to nine preparations; ***, p < 0.001, one-way ANOVA; Bonferoni post test. D, glutamate shifts the balance of GABAB receptor recycling and lysosomal degradation toward degradation without blocking recycling. Neurons were incubated for 1 h with 100 μm leupeptin, 100 μm chloroquine, or 0.5 μm bafilomycin A1 before inducing down-regulation of GABAB receptors by 50 μm glutamate or 50 μm monensin (blocks recycling by preventing fusion of intracellular vesicles with the plasma membrane) for 90 min. Living neurons were subsequently incubated with an antibody directed against the N terminus of GABAB2 to label cell-surface receptors and further processed for immunocytochemistry. Cell-surface fluorescence signals of individual neurons were quantified. Control, no treatment. Means ± S.E., n = 31–81 neurons derived from two to four independent experiments; n.s. = p > 0.05; **, p < 0.01, one-way ANOVA, Dunnett's post test.