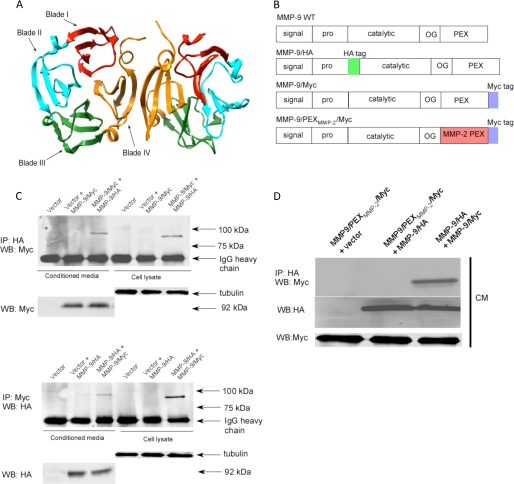
FIGURE 1.
MMP-9 homodimerizes through its PEX domain. A, ribbon diagram of the MMP-9 PEX domain (PDB code 1ITV). Homodimerization of MMP-9 is through the fourth blade of the MMP-9 PEX domain. B, schematic diagram of wild type MMP-9, MMP-9/HA, MMP-9/Myc, and MMP9/PEXMMP2/Myc. Five typical domains of MMP-9 from the N terminus to C terminus are the signal peptide (signal), propeptide (pro), catalytic domain (catalytic), hinge region (OG), and hemopexin-like domain (PEX). HA and Myc tags were inserted as shown. The PEX domain of MMP-9 was replaced by MMP-2 to generate MMP-9/PEXMMP-2/Myc. C, MMP-9 forms a homodimer in the COS-1 cells transfected with MMP-9 cDNAs. COS-1 cells were transfected with a combination of cDNAs as indicated. The conditioned medium (CM) and cell lysates were examined by a co-immunoprecipitation (IP) assay (upper panel) and a reciprocal co-immunoprecipitation assay (lower panel). 20 μg of total cell lysates or 20 μl of the conditioned medium were used as loading controls by anti-α/β-tubulin antibody for cell lysates and anti-Myc or anti-HA antibodies for the conditioned medium. D, replacement of the MMP-9 PEX domain with the corresponding region of MMP-2 prohibited dimerization with wild type MMP-9 as examined through a co-immunoprecipitation assay. The conditioned medium of COS-1 cells transfected with a combination of cDNAs as indicated was examined by a co-immunoprecipitation assay. 20 μl of the conditioned medium were examined by Western blotting (WB) using anti-Myc antibody for monitoring expression of MMP-9/Myc and MMP9/PEXMMP2/Myc.