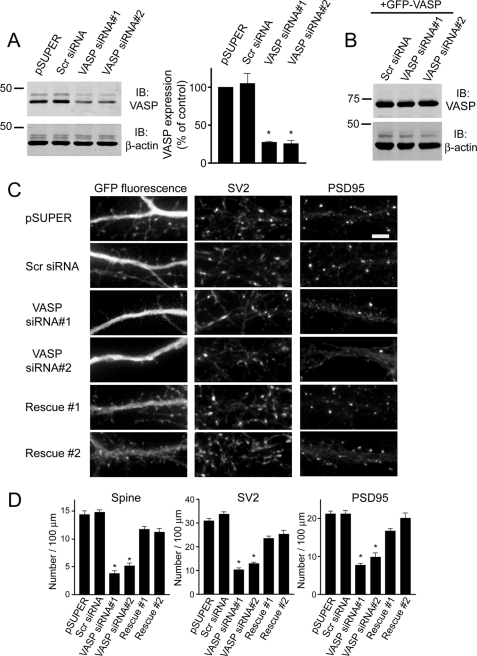
FIGURE 2.
Knockdown of endogenous VASP inhibits the formation of spines and synapses. A, cell lysates from R2Fs transfected with VASP siRNAs, pSUPER empty vector, or a non-silencing scrambled siRNA (Scr siRNA) were immunoblotted (IB) for VASP and β-actin (loading control). Quantification of blots from four separate experiments is shown (right panel). Error bars represent S.E. (*, p < 0.0001). B, cell lysates from R2Fs co-transfected with human GFP-VASP and scrambled siRNA (Scr siRNA) or VASP siRNAs were blotted for VASP and β-actin (loading control). C, neurons were co-transfected with GFP and either pSUPER empty vector, scrambled siRNA (Scr siRNA), or VASP siRNAs at day 6 in culture, fixed, and stained with synaptic markers at day 12. To show the siRNA-induced defect on spines and synapses was due to endogenous loss of VASP, neurons were co-transfected with human GFP-VASP and VASP siRNA#1 or VASP siRNA#2 (lower panels, Rescue #1 and Rescue #2). Bar, 5 μm. D, quantification of spine and synaptic density (SV2 and PSD95 clusters) in neurons transfected with the indicated constructs is shown. Error bars represent S.E. for 40–50 dendrites from at least three separate experiments (*, p < 0.0001). For panels A and D, asterisks denote a statistically significant difference compared with pSUPER-transfected cells.