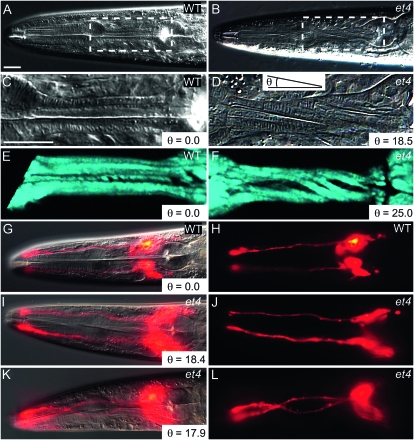
Figure 1.—
The Twp phenotype in the mig-6(et4) mutant. (A) The head of a wild-type animal, with the boxed area enlarged in C. Note that the pharyngeal structures are perfectly straight along the anterior–posterior axis. (B) The head of a mig-6(et4) mutant, with the boxed area enlarged in D. Note the torsion lines indicative of a twisted pharynx. The angle θ is defined here as that formed by the torsion lines of the muscles and the anterior–posterior axis, as shown in D. (E and F) A wild-type and mig-6(et4) mutant pharynx, respectively, imaged using SHG microscopy at successive focal planes and rendered three dimensionally. Note the twisted appearance of the muscles in the mutant. A wild-type worm stained with DiI is shown as an overlay of DIC and epifluorescence in G or epifluorescence only in H. Note that the DiI-filled amphid neurons are straight. (I–L) mig-6(et4) mutants similarly stained with DiI, with DIC and epifluorescence overlays in I and K and epifluorescence only in J and L. Note that one worm displays straight amphid neurons (I and J) while the other has twisted amphid neurons (K and L), even though both have twisted pharynges as indicated by the angle θ in I and K. Bars, 20 μm, with the bar in panel C applying to panels C through F, and the bar in panel A applying to all other panels.