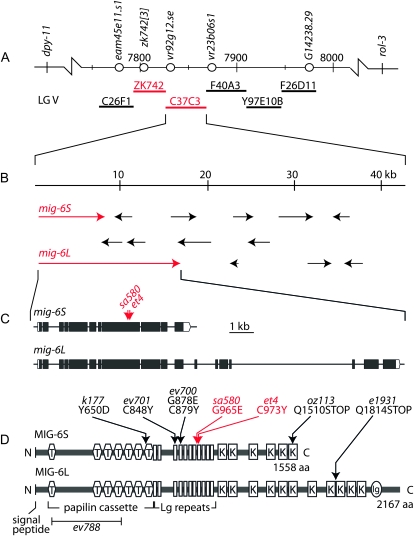
Figure 2.—
Mapping of the mig-6(et4) and mig-6(sa580) mutant alleles. (A) Part of the map for chromosome V, including the positions of the genetic markers used to map et4 and sa580. Single nucleotide polymorphisms that distinguish the wild-type N2 genome from the Hawaiian strain CB4856 are shown as open circles and the numbered positions refer to chromosomal locations expressed in kilobases. The locations of six cosmids that were tested for their ability to rescue the sa580 mutant are also shown (thick horizontal lines). The ZK742 and C37C3 cosmids could rescue the sa580 pharynx only when co-injected. (B) Enlarged view of the cosmid C37C3 showing genes as arrows and the two variants of the mig-6 gene in red. (C) Structure of the mig-6 gene showing the positions of the et4 and sa580 mutant alleles, which are both G-to-A transitions. (D) Domain structure of the MIG-6S and MIG-6L proteins, with the et4 and sa580 amino acid substitutions indicated by red arrows, and other mutant alleles by black arrows. T, thrombospondin domain; Lg repeats, lagrin repeats; K, Kunitz domain; and Ig, immunoglobulin domain. A signal peptide is also present at the N terminus of each protein.