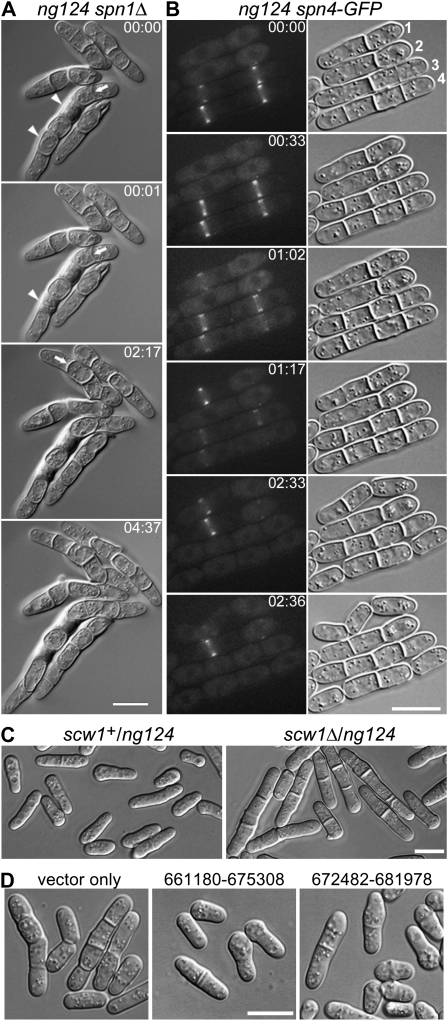
Figure 5.—
Characterization of mutant ng124 and its identification as an allele of scw1. (A and B) Selected DIC and fluorescence images are shown from time-lapse-microscopy series recorded at 1- or 2-min intervals; times are indicated in hours and minutes. The entire series can be viewed in File S3 and File S4. (A) Cell-separation defect in an ng124 spn1Δ double mutant. Strain JW321-1 was grown in YE5S medium at 30° and observed on YE5S at 24°. Arrows indicate abnormal-shaped septa; arrowheads indicate cells that appear to have lysed. (B) Apparently normal septin localization and variable cell-separation delay in an ng124 single mutant. Strain JW320 (ng124 spn4-GFP) was grown in EMM5S at 23° and observed on EMM5S at 24°. Cells are numbered for reference in the text. (C) Noncomplementation of ng124 and scw1Δ in diploid cells. Diploid strains JW2613 (scw1+/ng124) and JW2614 (scw1Δ/ng124) were observed by DIC microscopy after growth on YE5S-Ade at 25°. (D) Rescue of ng124 by plasmids containing scw1+. Strain JW2155 (ng124) was transformed with empty vector or with chromosome III plasmids that contain only scw1 (nucleotides 673,476–675,161) in their region of overlap (nucleotides 672,482–675,308), grown in EMM5S-Leu medium at 25°, and observed by DIC microscopy. Bars, 10 μm.