Figure 3.
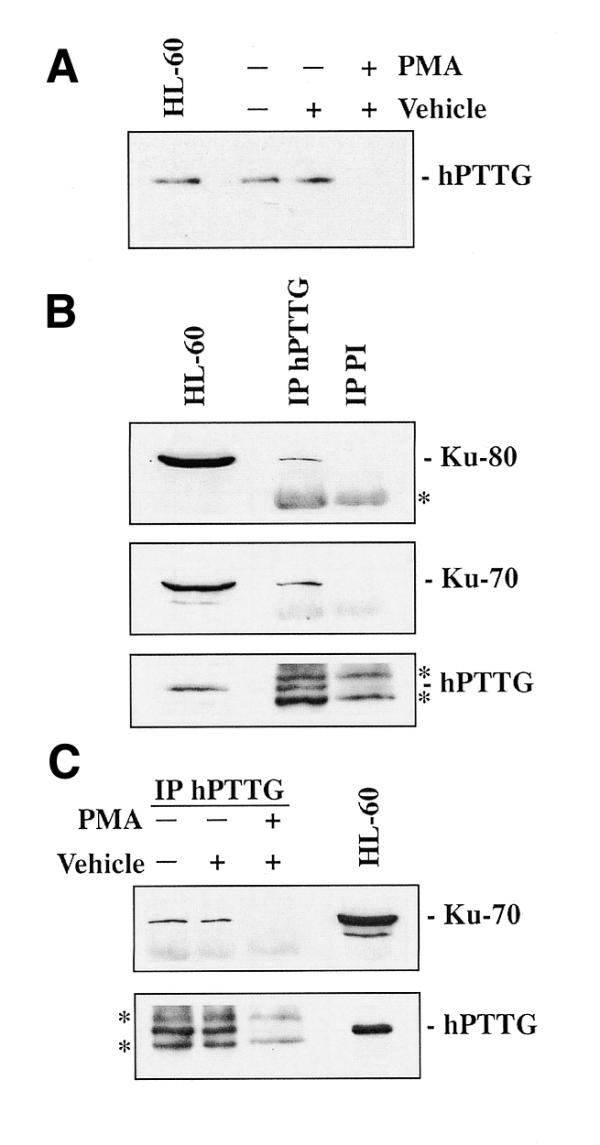
Binding of hPTTG to Ku-70 in intact cells. (A) Expression of hPTTG in differentiated and undifferentiated HL-60 cells. Equal amounts of total extracts from HL-60 cells treated with PMA (40 ng/ml), with the vehicle DMSO or untreated, were separated by SDS–PAGE, transferred to nitrocellulose filters and incubated with anti-hPTTG. HL-60, extract from 106 HL-60 cells. (B) Co-immunoprecipitation of hPTTG with Ku-70 and Ku-80 in undifferentiated HL-60 cells. Anti-hPTTG and preimmune (PI) sera were used to immunoprecipitate from NP-40 extracts of HL-60 cells (3 × 107 cells each). Complexes were resolved by SDS–PAGE, transferred to nitrocellulose filters and incubated with anti-Ku-70, anti-Ku-80 and anti-hPTTG. HL-60, extract from 106 HL-60 cells. (C) Study of the relevance of the hPTTG–Ku-70 interaction. Anti-hPTTG was used to immunoprecipitate from extracts of HL-60 cells (3 × 107) treated with PMA (40 ng/ml), the vehicle DMSO or untreated. Nitrocellulose filters were incubated with anti-Ku-70 and anti-hPTTG. HL-60, extract from 106 HL-60 cells. Asterisks indicate the IgG heavy and light chains.
