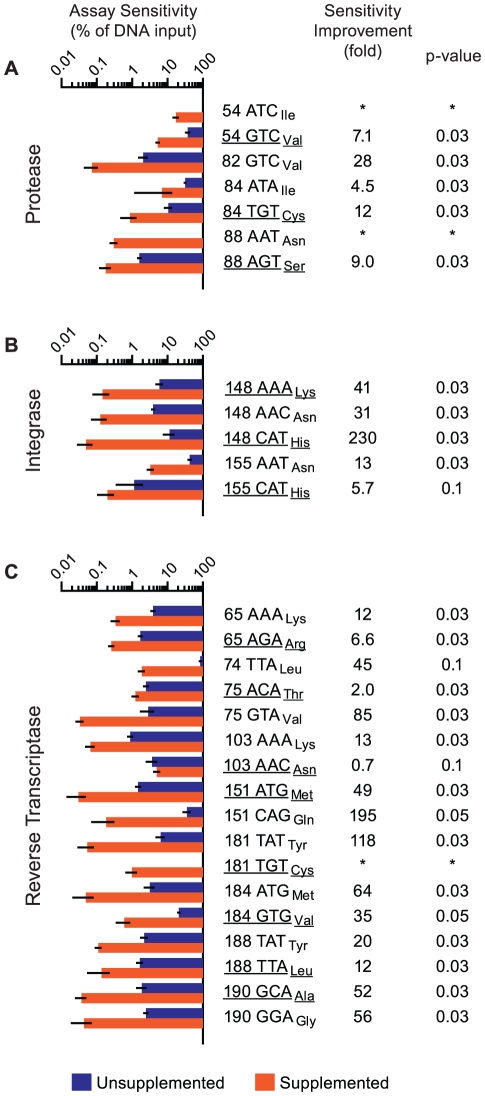
Figure 5. Duplex nucleator and competimer oligonucleotides improve assay sensitivity.
Abridged consensus subtype B HIV-1 Pol sequences containing all OLA probe binding sites were produced by ligase-mediated oligonucleotide assembly (Materials and Methods; Figure S3). Amplicons from these constructs differed only in the nucleotides corresponding to the drug resistance-associated codons. Each synthetic amplicon (solute) was diluted in series with another at the same concentration (solvent), used as templates in an ligase discrimination reaction and then subjected to bead hybridization (unsupplemented) or that with 25 nM competimer and 2.5 nM duplex nucleator oligonucleotides (supplemented). Assay sensitivity values reflect the minimal solute template content (%) required to elicit the cutoff value for the unsupplemented (blue bars) and supplemented assay (orange bars) (all +/−s.d., N = 4 independent experiments). Codons associated with drug resistance are underlined. Fold sensitivity improvement values >1 reflect detections where oligonucleotide supplementation gave a lower sensitivity value (middle column). Mann-Whitney Rank Sum Test p-values are shown at the right. Assay sensitivity for (A) seven codon sequences in PR, (B) five codon sequences in IN and (C) seventeen codon sequences in RT. *Sensitivity improvements could not be determined for codons PR 54 ATCIle, PR 88 AATAsn and RT 181 TGTCys because these codons were undetectable in the unsupplemented assay.