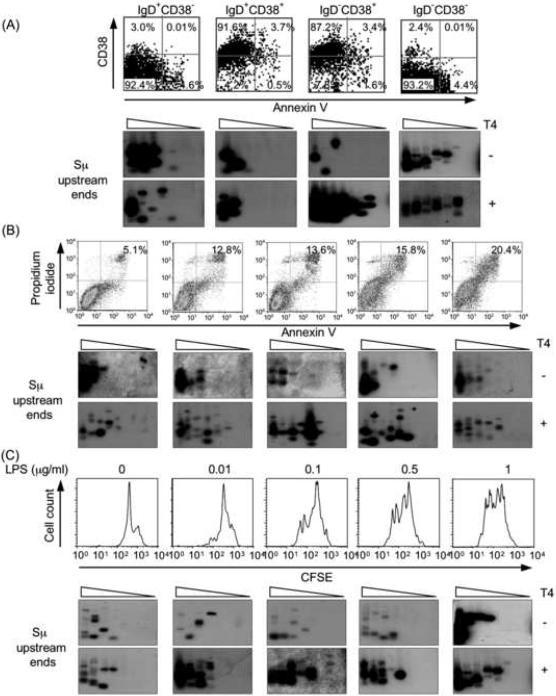
Fig. 3.
Cell apoptosis or proliferation has no significant impact on specific Sμ DSB detection. A, Purified IgD+CD38−, IgD+CD38+, IgD−CD38+ and IgD−CD38− B cell fractions contain negligible proportions of apoptotic cells. Human tonsil IgD+CD38−, IgD+CD38+, IgD−CD38+ and IgD−CD38−B lymphocyte fractions were analyzed for their content in apoptotic cells (upper and lower right quadrants) using the Annexin V Apoptosis Detection Kit (Oncogene Research Products, Inc., San Diego, CA) and flow cytometry. Blunt and total (blunt plus staggered) Sμ upstream DSB ends were detected by specific LM-PCR in each B cell subset DNA after pre-treatment with nil (T4−) or T4 pol (T4+). B, Apoptosis does not affect specific Sμ DSB detection. 4B6 cells were cultured in RPMI-1640 medium supplemented with 10% FBS for 24 hr or 0% FBS for 12, 24, 48, and 72 hr (left to right panels) and then analyzed for apoptosis by Annexin V-FITC and propidium iodide staining in flow cytometry. Apoptotic cells accounted for 5.1%, 12.8%, 13.6%, 15.8% and 20.4% of each subset (left to right panels). Blunt and total (blunt plus staggered) Sμ upstream DSB ends were detected by LM-PCR after pre-treatment with nil (T4−) or T4 pol (T4+), respectively. No correlation was observed between degree of apoptosis and specific detection of DSBs in Sμ DNA. C, Differential cell proliferation does not affect specific Sμ DSB detection. Freshly isolated mouse spleen B cells were stained with 5 μg/ml CFSE at 37°C for 10 min. After washing, cells were cultured in the presence of LPS (0, 0.01, 0.1, 0.5 and 1 μg/ml) in triplicate in 24-well flat-bottom plates at the density of 1 × 106 cells/ml for 42 hr, and analyzed by flow cytometry. Blunt and total Sμ upstream DSB ends were detected by LM-PCR after pre-treatment with nil (T4−) or T4 pol (T4+). For LM-PCR, samples consisted of 8, 4, 2, 1, 0.5, 0.25, 0.125, and 0.0625 ng of linker-ligated DNA derived from 1280, 640, 320, 160, 80, 40, 20, and 10 B cells.