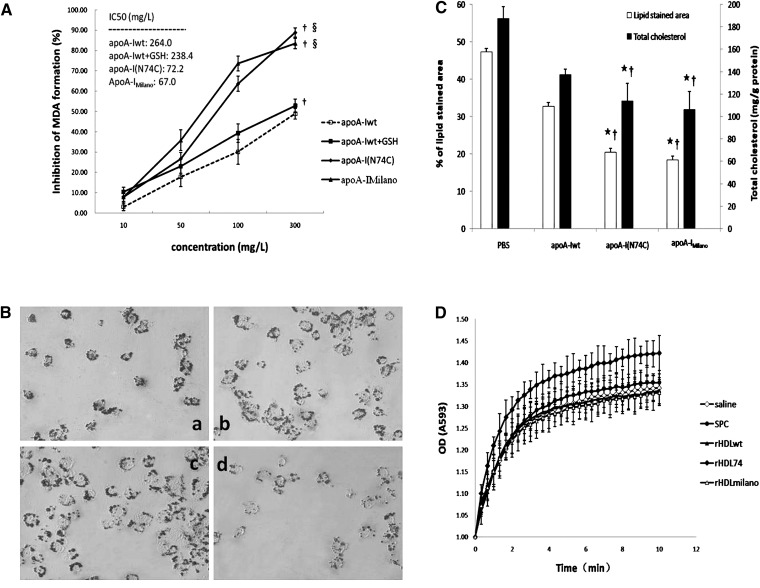
Fig. 1.
Antioxidant activity of apoA-I(N74C) in lipid-free state in vitro and in lipid-bound state in vivo. A: Potent inhibitory effect of recombinant apolipoproteins against LDL oxidation in the presence of 5 μM CuSO4 in vitro. Freshly prepared LDL (100 mg/l) was incubated with each apolipoprotein (10–300 mg/l) for 4 h at 37°C. After incubation, samples were assayed for MDA formation and expressed as percentage of inhibition relative to the Cu2+-only controls. The IC50 values were calculated from the linear slopes of the graphs. To preclude the effects of thiols induced by cysteine mutation, the same molar concentrations of GSH as the apolipoproteins tested were added to apoA-Iwt reaction system and analyzed the antioxidant effects. B: The Oil Red O staining in THP-1-derived macrophages treated with PBS at 40× magnification: (a) apoA-Iwt (control); (b) apoA-Iwt + GSH; (c) apoA-I(N74C); and (d) apoA-IMilano. C: Quantitative analysis of the intracellular lipid accumulation in THP-1-derived macrophages. The areas of Oil Red O staining were calculated using the Image-Pro Plus software. To verify the data of lipid staining area, the intracellular total cholesterol level expressed as the ratio between total cholesterol and total protein was analyzed. D: Antioxidant ability of mice serum measured by FRAS. Absorption of rHDL74-injected serum at 593 nm for up to 10 min exhibited of up to 42% more than the initial values. Data are expressed as mean ± SD. ★P < 0.05 versus PBS; †P < 0.05 versus apoA-Iwt; §P < 0.01 versus apoA-Iwt + GSH. Apo, apolipoprotein; apoA-I(N74C), apolipoprotein A-I(N74C); apoA-Iwt, wild-type apoA-I; FRAS, ferric reducing ability of serum; GSH, L-glutathione; rHDL, recombinant HDL; IC50, half-maximal inhibitory concentration; MDA, malondialdehyde.