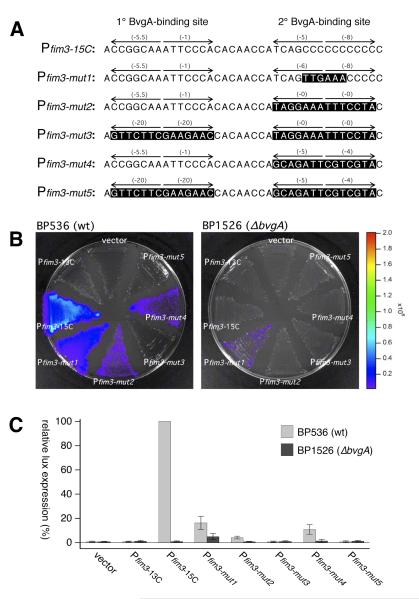
Fig. 4. Effects of DNA sequence substitutions in the fim3 promoter.
A) The sequences of the fim3 wild type promoter and derivatives substituted with specific sequences at the secondary BvgA-binding site that are predicted to mediate interaction with region 4.2 of the sigma subunit of RNA polymerase (Pfim3-mut1) or increased binding of BvgA~P (Pfim3-mut2 – Pfim3-mut5). Pfim3-mut1 contains a near-consensus −35 region. Pfim3-mut2 and Pfim3-mut3 contain the primary binding site of the fha promoter in place of the secondary binding site of Pfim3. Pfim3-mut4 and Pfim3-mut5 contain a binding site from the ptx promoter in place of the secondary binding site of Pfim3. In Pfim3-mut3 and Pfim3-mut5, the primary binding site has been destroyed by substitution with a sequence of identical length in which every nucleotide has been changed to a least-productive alternative, according to the table in Fig. 2C. Constructs with Pfim3-15C and Pfim3-13C were included as positive and negative controls, respectively. B&C) Activities of wild type and substituted promoters were analyzed for their abilities to promote lux transcription in B. pertussis strains containing the wildtype bvg locus (BP536) or a bvgA deletion (BP1526). Intensity of light production after growth on BG agar is depicted in a false-color image (B) and by quantitative data derived from the analysis of several such images (C).