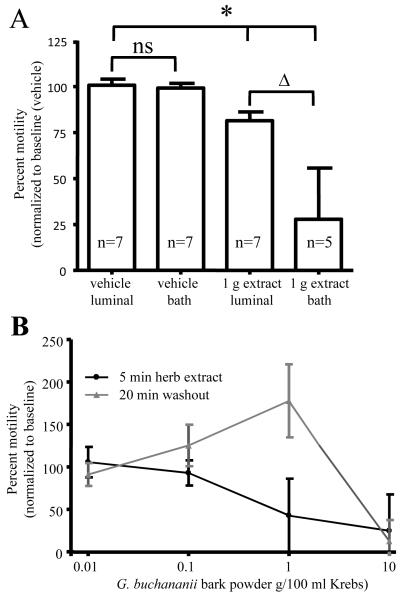
Figure 1.
Intraluminal and bath applications of G. buchananii bark extract inhibit pellet propulsion in isolated segments of guinea pig distal colon. A. Bar graph showing the effects of intraluminal vs. bath delivery of the extract (1 g bark powder/100 ml Krebs solution; 5 minute application) on propulsive motility. No difference was detected between intraluminal and bath applications of the vehicle with regard to pellet velocity (bracket with ns). Intraluminal and bath extract applications reduced pellet velocity (bracket with asterisks). 1 g powder in 100 ml Krebs had larger inhibitory effects when applied in the bath vs. an intraluminal delivery (bracket with triangle). B. The concentration-dependent effects of the extract and the effects of washout on pellet propulsion. Lower concentrations (0.01- 0.1 g bark powder/100 ml Krebs) did not alter motility. Higher concentrations (1 - 10 g/100 ml Krebs) inhibited propulsion in a concentration-dependent fashion. At concentrations of 1 g bark powder/100 ml Krebs and below, pellet propulsion was rapidly restored to normal values and an increased rate of propulsive motility (30-100% above baseline) was observed following washout for 10-20 min. Normal pellet propulsion was not restored by 20 min. of washout after treatment with G. buchananii bark powder at a concentration of 10 g/100 ml Krebs.