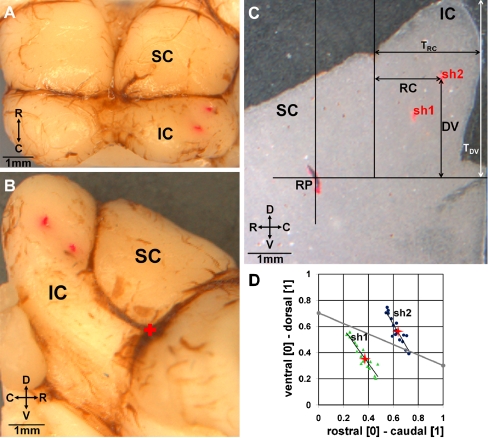
FIG. 3.
Reconstruction of the AMI array placements in the inferior colliculus (IC) for one animal. A View of the dorsal surface of the IC and superior colliculus (SC). The two red dots indicate where we inserted the AMI array. B Lateral view of the right IC and SC in which the red plus sign represents the location of our reference point (RP) used for normalizing the array locations across animals. C A 40-μm-thick sagittal slice detailing our coordinate system used to quantify the location of the trajectory for each array placement (appears as dots in each slice since the array was inserted at a 45º angle to the sagittal plane). D The normalized coordinates (RC divided by TRC, DV divided by TDV) are plotted across several slices (dots) for each trajectory (placement 1: green, placement 2: blue). Since these coordinates systematically change across slices, we only selected the values for the slice corresponding to 0.54 from the lateral edge to the midline (red pluses) that were then later displayed on a single plot across all animals. The red pluses in D correspond to the red dots caused by the track of the AMI in C. The gray line in D divides which locations we labeled as caudal (above the line) and rostral (below the line) and was based on the threshold values shown in Figure 6. For further details on our reconstruction and grouping methods, see Methods: “ICC probe histology and site locations”. C caudal, D dorsal, R rostral, V ventral.