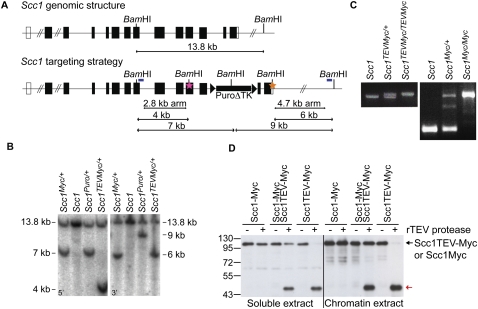
Figure 2.
Generation of a TEV-cleavable Scc1 allele. (A) Targeting strategy for generating an Scc1TEVMyc allele. Schematic of the Scc1 genomic locus and targeted alleles (Scc1TEVMyc or Scc1Myc). The pink star indicates three tandem TEV protease recognition sites, including a novel BamHI restriction site, that were inserted into exon 11. The orange star indicates a c-Myc10 epitope, including a novel BamHI restriction site that was inserted before the Stop codon. The relative location of the 5′ and 3′ probes (blue bars) and BamHI sites that were used in Southern blot analysis are shown on the targeted locus. (B) Southern blot analysis of wild-type (Scc1) and heterozygous (Scc1TEVMyc/+ and Scc1Myc/+) mouse ES gDNA digested with BamHI and hybridized with 5′ and 3′ probes to check for homologous recombination. (C) PCR analysis of wild-type (Scc1), heterozygous (Scc1TEVMyc/+), and homozygous (Scc1TEVMyc/TEVMyc) mouse ear gDNA (left panel), and wild-type (Scc1), heterozygous (Scc1Myc/+), and homozygous (Scc1Myc/Myc) mouse ear gDNA (right panel). (D) Western blot analysis of Scc1 cleavage by recombinant TEV protease in soluble and chromatin extracts from Scc1Myc/Myc, Scc1Myc/TEVMyc, and Scc1TEVMyc/TEVMyc ES cells. Scc1TEV-Myc and Scc1-Myc were detected by anti-c-Myc antibody. The red arrow indicates the Scc1 cleavage fragment.