Figure 1. α- and β1- subunit of the BK channel.
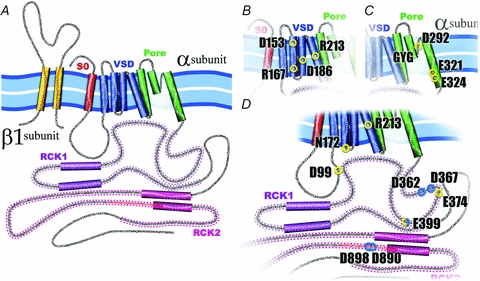
A, the α-subunit of the BK channel is formed by 7 transmembrane (S0–S6) segments and a large C-terminus. Segments S1–S4 have been implicated in voltage sensing whereas S5 and S6 form the conduction pore. S0 plays an important role in the functional coupling between α- and β1-subunit. The C-terminus contains two putative RCK domains where the Ca2+ and Mg2+ binding sites are located. All BK β subunits contain two transmembrane segments leaving their N- and C-terminus oriented towards the interior of the cell. B, voltage sensor domain (VSD). BK's VSD is positioned between the TM segments S1–S4, and four charged residues contribute to the channel voltage membrane sensitivity, D153 and R167 in the S2, D186 in the S3 and R213 in the S4. C, the pore. Three residues have been identified in BK pore as partially responsible for the channel high conductance, D292, E321 and E324. Additionally, in the pore, as in the majority of K+ channels, is located the signature sequence GYG, responsible for the high K+ selectivity of this channels. D, Ca2+ and Mg2+ sites. Spread throughout in the BK cytoplasmatic domain are located the high affinity Ca2+ sites, D362, D367 (in the RCK1), D898 and D890 (in the denominated calcium bowl in the RCK2), and the low affinity Ca2+ site, E399 (RCK1), which is shared with the site that coordinate Mg2+, D99 and N172 in the VSD, and E372 and E399 in the RCK1. The residue R213 showed here is electrostatically affected by the Mg2+ binding.
