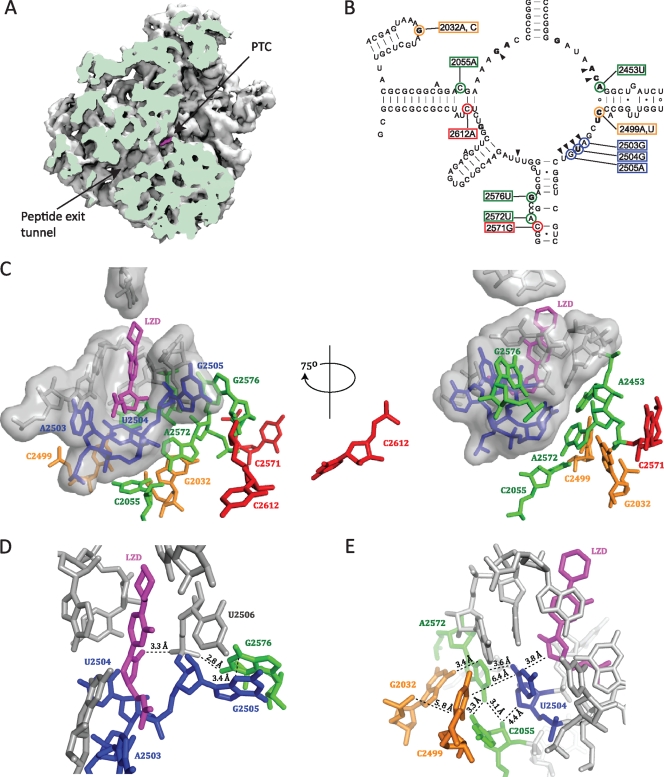
FIG. 1.
The positions of mutated 23S rRNA nucleotides relative to the linezolid binding site. (A) A cut view of the D. radiodurans 50S subunit showing linezolid (magenta) bound at the PTC and the peptide exit tunnel (PDB accession number 3DLL [49]). The image was made with the VMD software program (19) and contributed by Jacob Pøhlsgaard. (B) Secondary structure of the M. smegmatis 23S rRNA peptidyl transferase loop. The positions of mutated nucleotides are highlighted with colored circles, and the corresponding E. coli numbering is boxed in colored rectangles. The coloring of mutations indicates first-layer (blue), second-layer (green), third-layer (orange), and outer-layer (red) nucleotides with respect to linezolid. Wedges point to first-layer nucleotides that form the linezolid binding pocket. Nucleotides in bold type are those where a mutation(s) is identified to confer linezolid resistance in at least one organism (1, 14, 22, 30, 33, 43, 52, 53). (C to E) Close-up views of the linezolid binding site made with the PyMOL software program (7), where nucleotides are colored as described above. (C) The locations of mutated nucleotides with respect to bound linezolid. First-layer nucleotides are shown in surface representation. (D) The position of G2576 with respect to linezolid. (E) The positions of the nucleotides involved in the double mutations with respect to linezolid.