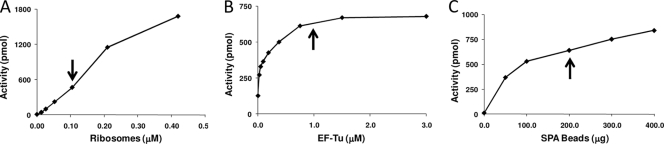
FIG. 1.
Optimization of the coupled aminoacylation/translation (A/T) assay. (A) Titration of E. coli ribosomes in the A/T protein synthesis system assay. Ribosomes (0.013 to 0.42 μM) were assayed in the presence of saturating amounts of the other components. The arrow indicates the concentration of ribosomes used in the screening assay. (B) Plot of poly(Phe) synthesis as a function of increasing concentrations of E. coli EF-Tu (0.023 to 3.0 μM) in the A/T system. The arrow indicates the concentration of EF-Tu used in the screening assay. (C) Determination of the amount of SPA beads needed to quantify the signal from poly(Phe) synthesis in the A/T reactions. The arrow indicates the amount of SPA beads used in the screening reactions.