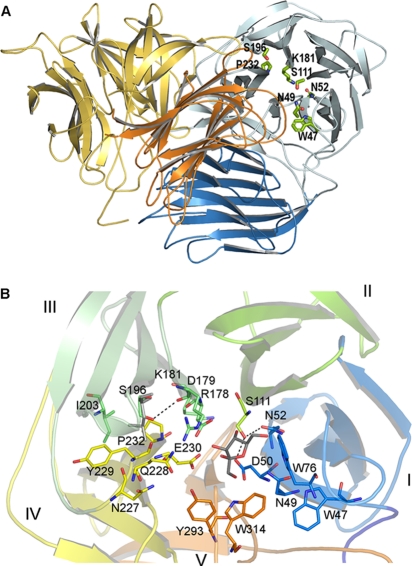
FIG. 3.
(A) Cartoon of the three-dimensional structure of the S. occidentalis Ffase. Two monomers (blue and orange) associate to form a tight dimer through mainly polar and hydrophobic interactions. The two domains within each monomer are shaded distinctly. The residues investigated in this work are represented as sticks. (B) The catalytic domain folds into a propeller made up of five blades (I to V), each represented in a different color. The residues mentioned in the text are shown as sticks with the same color code. Fructose in the Ffase active site is represented in grey. Asp50 (NDPNG), Asp179 (RDP), and Glu230 (EC) are the catalytic residues. The putative position of a modeled Leu196 is represented in grey.