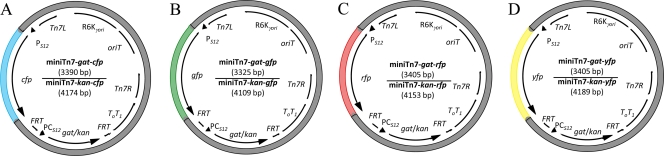
FIG. 1.
Maps of mini-Tn7-gat-cfp and mini-Tn7-kan-cfp (A), mini-Tn7-gat-gfp and mini-Tn7-kan-gfp (B), mini-Tn7-gat-rfp and mini-Tn7-kan-rfp (C), and mini-Tn7-gat-yfp and mini-Tn7-kan-yfp (D). These constructs allow for site-specific transposition of fluorescent protein genes (cfp, gfp, rfp, and yfp), using the nonantibiotic glyphosate resistance marker (gat) or the kanamycin resistance marker (kan) assisted by the helper plasmid pTNS3-asdEc. Differences in plasmid size are indicated in parenthesis. The PS12 promoter drives all fluorescent proteins. The gat or kan cassette is driven by the rpsL promoter of B. cenocepacia (PCS12) on all constructs. These selectable markers are flanked by FRT sequences for Flp protein-mediated excision. Abbreviations: oriT, RP4 conjugal origin of transfer; PCS12, rpsL promoter of B. cenocepacia; PS12, rpsL promoter of B. pseudomallei; R6Kγori, π protein-dependent R6K origin of replication (γ indicates subtype of the origin); Tn7L and Tn7R, left and right transposase recognition sequences; T0T1, transcriptional terminator.