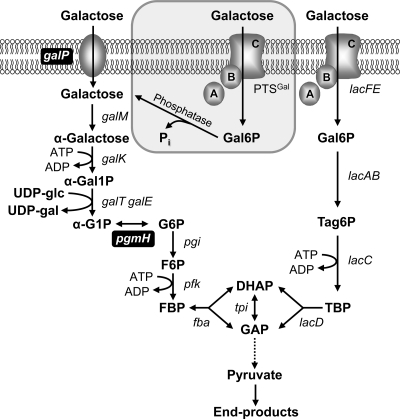
FIG. 1.
Schematic overview of the alternative routes for galactose uptake and further catabolism in L. lactis. Galactose can be imported by the non-PTS permease GalP and metabolized via the Leloir pathway (galMKTE) to α-G1P, which is converted to the glycolytic intermediate G6P by α-phosphoglucomutase (pgmH). Alternatively, galactose can be imported by PTSLac (lacFE) and further metabolized to triose phosphates by the Tag6P pathway (lacABCD). Here, we propose a new uptake route consisting of galactose translocation via the galactose PTS, followed by dephosphorylation of the internalized Gal6P to galactose, which is further metabolized via the Leloir pathway (highlighted in the gray box). galP, galactose permease; galM, galactose mutarotase; galK, galactokinase; galT, galactose 1-phosphate uridylyltransferase; galE, UDP-galactose-4-epimerase; pgmH, α-phosphoglucomutase; lacAB, galactose 6-phosphate isomerase; lacC, Tag6P kinase; lacD, tagatose 1,6-bisphosphate aldolase; lacFE, PTSLac; PTSGal, unidentified galactose PTS; Phosphatase; unidentified Gal6P-phosphatase; pgi, phosphoglucose isomerase; pfk, 6-phosphofructo-1-kinase; fba, fructose 1,6-bisphosphate aldolase; tpi, triose phosphate isomerase; α-Gal1P, α-galactose 1-phosphate; α-G1P, α-glucose 1-phosphate; UDP-gal, UDP-galactose; UDP-glc, UDP-glucose; G6P, glucose 6-phosphate; Gal6P, galactose 6-phosphate; Tag6P, tagatose 6-phosphate; TBP, tagatose 1,6-bisphosphate; FBP, fructose 1,6-bisphosphate; DHAP, dihydroxyacetone phosphate; GAP, glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate. The dotted arrow represents the conversions of GAP to pyruvate via the glycolytic pathway. Steps essential to improve galactose consumption are shown in black boxes.