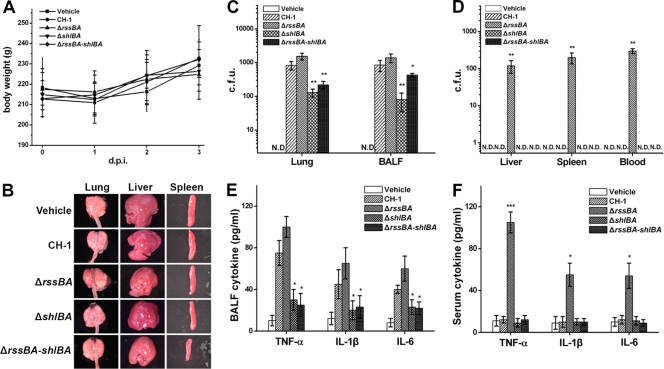
FIG. 5.
The rssBA deletion leads to systemic infection of S. marcescens in a sublethal-pneumonia model of immunocompetent rats. Rats (n = 6 in each group for independent experiments) were i.t. infected with 1 × 105 CFU of S. marcescens CH-1, S. marcescens ΔrssBA, S. marcescens ΔshlBA, and S. marcescens ΔrssBA-shlBA cells for 3 days postinfection (d.p.i.). Normal saline was used as a vehicle control. (A) Body weight was monitored daily. (B) On the third day p.i., the rats were sacrificed, and organs, including lungs, livers, and spleens, were removed for gross morphology observation accompanied by collection of BALF and sera. (C and D) The bacterial loads of organ homogenates, sera, and BALF were determined as the average number of CFU per gram of organ and per ml of serum or BALF. N.D., not detectable. (E and F) BALF and sera from each group 3 days p.i. were utilized to measure TNF-α, IL-1β, and IL-6 as determined by ELISA. All results are shown as the average of three independent experiments, with the standard deviations indicated by error bars. *, P < 0.05, and **, P < 0.01 in comparison to CH-1 (Student's t test).