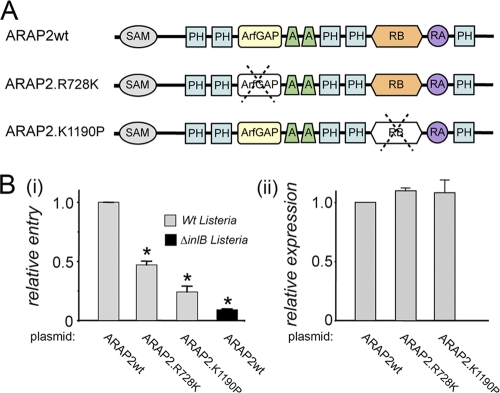
FIG. 4.
The ArfGAP and Rho binding domains of ARAP2 promote entry of Listeria. (A) Domains present in ARAP2 and locations of R728K and K1190P mutations. SAM, sterile α motif; PH, pleckstrin homology domain; ArfGAP, Arf GTPase-activating protein; A, ankyrin repeat; RB, Rho binding domain; RA, Ras-associating domain. Top diagram, wild-type (wt) ARAP2. Bottom two diagrams, ARAP2 alleles R728K and K1190P, containing single amino acid substitutions that inactivate the ArfGAP and RhoA binding domains, respectively. (B) Effect of mutations in the ArfGAP or Rho binding domain on bacterial internalization. HeLa cells were transfected with plasmids expressing Flag-tagged wild-type (wt) ARAP2 or ARAP2 alleles containing the R728K or K1190 mutation. Panel i, at approximately 24 h posttransfection, entry of Listeria was assessed using a fluorescence microscopy-based assay (38). Data are averages ± SD from four experiments. *, P < 0.001 compared to the ARAP2wt control. Panel ii, expression of the Flag-tagged ARAP2 alleles was measured using confocal microscopy (see Materials and Methods). P = 0.32 (not significant).