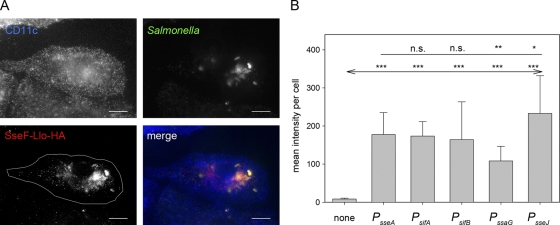
FIG. 4.
Translocation of fusion proteins by intracellular Salmonella. WT S. enterica serovar Typhimurium harboring plasmids with cassettes for the expression of sseF::lisA::HA under the control of various promoters was used to infect BM-DC at an MOI of 25. The cells were fixed 16 h after infection and processed for immunostaining for DC marker CD11c (blue), intracellular Salmonella (green), and translocated fusion protein SseF-Llo-HA (red). CD11c+ and Salmonella-infected cells were identified by confocal laser scanning microscopy and imaged by using the ZEN software package (Zeiss). (A) Representative infected BM-DC with Salmonella WT harboring an expression cassette with PsseJ translocating SseF-Llo-HA. The white line in the SseF-Llo-HA micrograph defines the area used for quantification of the immunofluorescence signals. (B) After infection with Salmonella WT harboring plasmids with various expression cassettes, infected cells with similar amounts of intracellular Salmonella were selected for the various conditions, and the signal intensities of the Cy3 channel for the anti-HA strains were measured with identical exposure times. The mean signal intensities and standard deviations for at least 20 infected cells per strains are shown. Statistical analyses were performed comparing signals for expression cassettes with various promoters to signals for expression cassettes with PsseA (indicated by a plain line) or by comparison to mock-infected cells (indicated by a line with arrows). Statistical analysis: n.s., not significant; *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001.