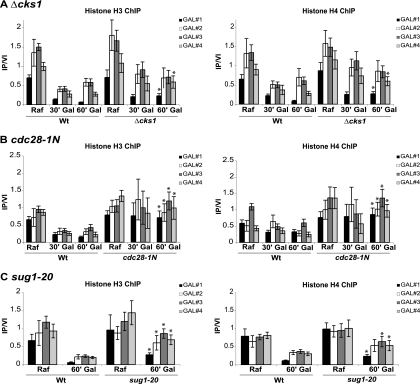
FIG. 1.
cks1, cdk1, and proteasome mutations confer an abnormally high histone density at the GAL1 promoter and open reading frame (ORF). Chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) was performed using histone H3 and histone H4 antibodies, respectively. In each case, GAL1 was induced for the indicated time (30 min [30′] or 60 min [60′]) by the addition of galactose (Gal) to cultures growing on raffinose (Raf). Chromatin immunoprecipitations were analyzed using four primer sets where GAL#1 is within the GAL1 promoter region and GAL#2, GAL#3, and GAL#4 span the GAL1 ORF. Immunoprecipitated signals were normalized using a primer set corresponding an untranscribed region of chromosome VI (IP/VI). (A) The wild type (Wt) and cks1 deletion mutant (Δcks1) were compared in an experiment carried out at 30°C. (B) The wild type and a cdk1 mutant specifically defective in Cks1 binding (cdc28-1N) were compared in an experiment carried out at 25°C. (C) sug1-20 is a temperature-sensitive mutation of the RPT6 gene encoding a proteasomal ATPase subunit. The experiment was carried out after shifting cultures from 25°C to 30°C for 5 h. Values are means ± standard deviations (SDs) (error bars). Asterisks indicate statistically significant differences (Student's t test) when comparing the values for the wild type and mutant 60 min after the addition of galactose. P values are given in Table 3. PCR primer sequences are provided in Table 2.