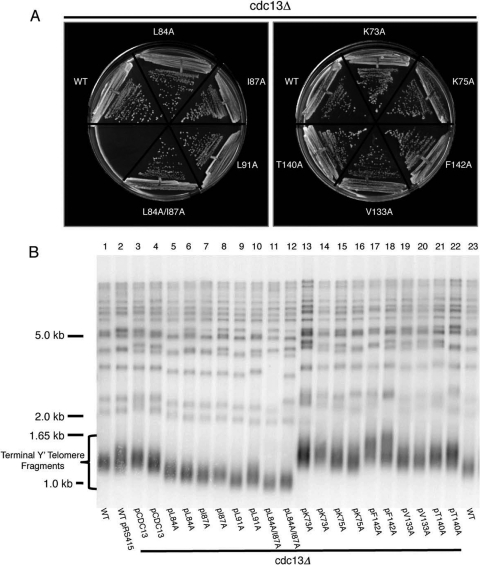
FIG. 5.
Functional assays of Cdc13N dimerization and DNA binding mutants. (A) Cdc13N dimerization and DNA binding mutants expressed from the CDC13 promoter support normal growth in cdc13Δ mutants. CDC13/cdc13Δ diploids were transformed with the indicated plasmids, and haploid cdc13Δ cells were obtained via sporulation. The cells shown had grown for ∼90 generations from spore germination. WT, cdc13Δ cells carrying the wild-type CDC13 plasmid. (B) Telomere Southern blot analysis of Cdc13N point mutants that affect dimerization or DNA binding. XhoI-digested DNA was blotted and probed for telomere repeat DNA. Cells were obtained as described above, and two independent spore products were examined for each plasmid. Also shown are samples from wild-type cells (the same sample is loaded in lanes 1 and 23) and wild-type cells carrying the vector (lane 2).