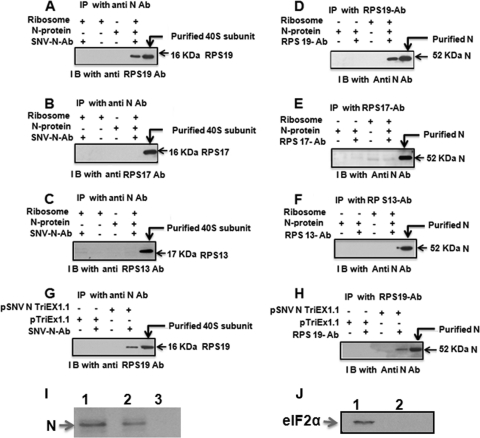
FIG. 3.
Purified 40S ribosomal subunits were treated with RNase A and incubated with bacterially expressed and purified N. The reaction mixture was immunoprecipitated (IP) with anti-N antibody and examined by anti-RPS19 antibody (A), anti-RPS17 antibody (B), or anti-RPS13 antibody (C). Conversely, immunoprecipitation was carried out with anti-RPS19 antibody (D), anti-RPS17 antibody, (E) or anti-RPS13 antibody (F) followed by Western immunoblot (I B) analysis with anti-N antibody. Cell lysate from HeLa cells transfected with N expression plasmid (pSNV N TriEx1.1) or empty vector (pTriEx1.1) was treated with RNase A to degrade the total RNA, including 18S rRNA. After RNase A treatment, cell lysate was immunoprecipitated with anti-N antibody, and the immunoprecipitated material was examined by Western blot analysis using anti-RSP19 antibody (G). Conversely, immunoprecipitation was carried out with anti-RPS19 antibody, followed by Western blot analysis using anti-N antibody (H). In panel I, the 40S ribosomal subunit was purified from HeLa cells expressing N. The purified 40S subunit was run on SDS-PAGE and transferred to a PVDF membrane. Western blot analysis was carried out using anti-N antibody. Bacterially expressed and purified N was used as the positive control (lane 1). Purified 40S subunits from HeLa cells transfected with N expression plasmid (lane 2) or transfected with the empty vector (lane 3) clearly show that N remains associated with the 40S subunit. Purified 40S subunits from panel I were examined for the presence of eIF2α by Western blotting using anti-eIF2α antibody (J). Cell lysate from HeLa cells expressing N was used as the positive control (lane 1). Purified 40S subunits prepared from HeLa cells expressing N (lane 2) clearly show that eIF2α is not copurified along with 40S subunits.