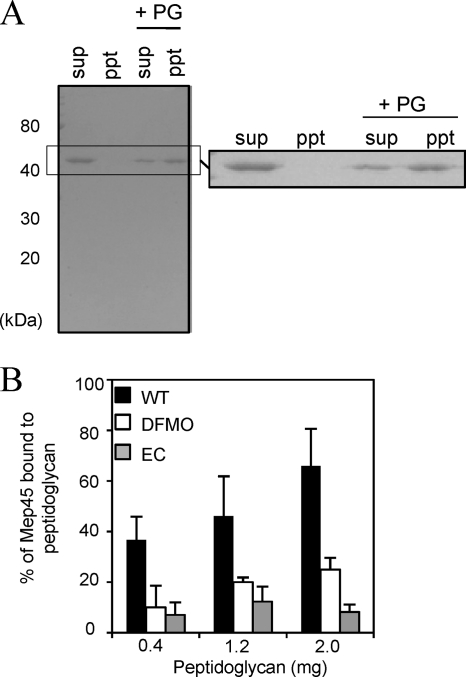
FIG. 2.
In vitro peptidoglycan-binding assay. (A) Western immunoblot of Mep45 binding to wild-type S. ruminantium peptidoglycan. Solubilized Mep45 (3 μg) was mixed with or without 1 mg of purified peptidoglycan (PG). The peptidoglycan-associated Mep45 (ppt) and non-peptidoglycan-associated Mep45 in the supernatant fraction (sup) were detected by using anti-Mep45 antiserum. (B) Effect of the PG-cadaverine on the interaction between Mep45 and peptidoglycan. Relative amounts of peptidoglycan-associated Mep45 were quantified densitometrically following immunoblotting. Solubilized Mep45 (5 μg) was incubated with 0.4, 1.2, or 2.0 mg of purified peptidoglycan from (i) wild-type S. ruminantium cells (WT [closed bars]), (ii) S. ruminantium cells cultivated in the presence of 10 mM DFMO (open bars), and (iii) the E. coli lpo mutant (EC [shaded bars]). The values represent the ratio of the amount of Mep45 after binding to peptidoglycan over the initial amount (mean ± standard deviation [SD] of triplicate experiments).