Table 1.
Oxyaminations of styrenes using 6.a
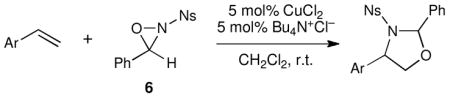 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| entry | styrene | product | time | yield |
| 1 | 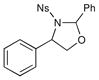 |
3 h | 75% | |
| 2 | 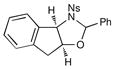 |
45 min | 52% | |
| 3 | 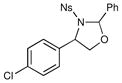 |
3 h | 54% | |
| 4 | 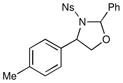 |
1 h | 70% | |
| 5 | 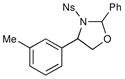 |
3 h | 75% | |
| 6 | 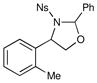 |
2.5 h | 65% | |
| 7 | 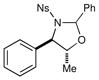 |
1 h | 84% | |
| 8 | 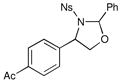 |
1.5 h | 59% | |
Conditions: 1 equiv of styrene, 1.5 equiv of 6, 5 mol% CuCl2, 5 mol% Bu4N+Cl−, CH2Cl2 (0.2 M in styrene), ambient temperature.
