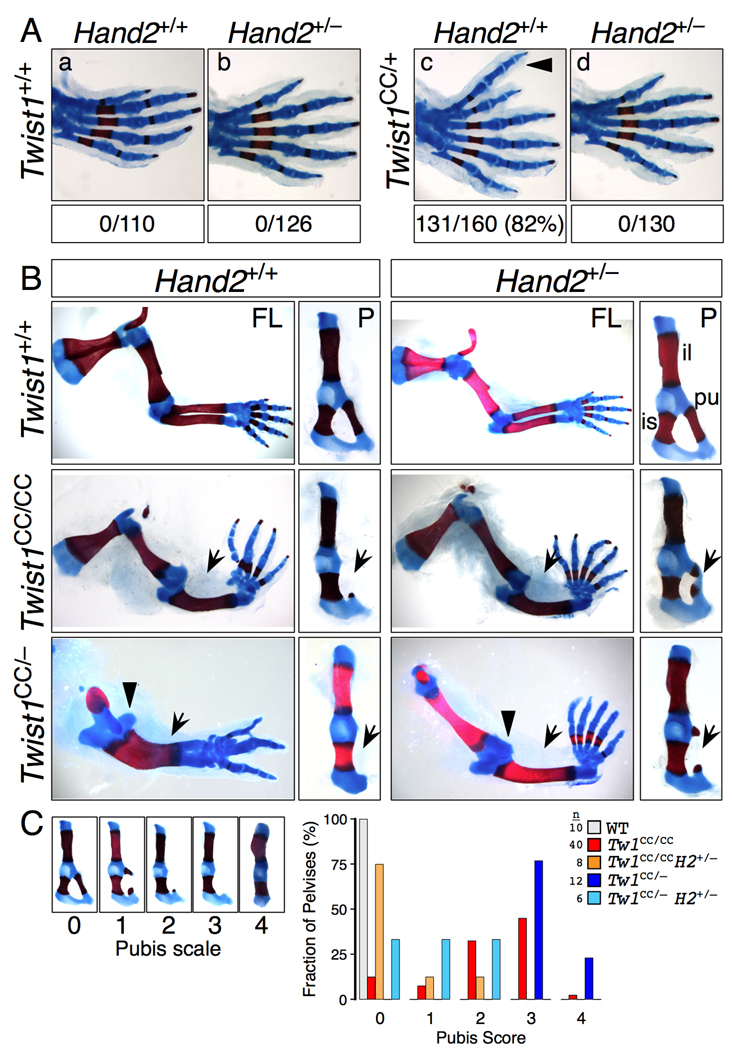
Figure 2. Genetic interactions between Twist1CC and Hand2.
(A) Twist1CC/+ hindlimb polydactyly is sensitive to Hand2 dosage. Hindlimbs of F1 progeny of Twist1CC/+; Hand2+/+ X Twist1+/+; Hand2+/− intercross scored for preaxial polydactyly (arrowhead) show complete suppression of polydactyly in double heterozygotes (p<0.001, chi squared).
(B) Twist1CC forelimb and pelvis phenotypes are sensitive to Hand2 dosage. Hand2 null allele was crossed onto compound Twist1 genotypes as indicated. Twist1CC/CC limbs with reduced Hand2 gene dosage (row 2) have less severe pubis hypoplasia (P columns, arrows) but still display radial aplasia (FL columns, arrows). Twist1CC/− limbs with reduced Hand2 gene dosage (row 3) resemble less severe Twist1CC/CC limbs, with duplicated ulnae replaced by radial aplasia (FL columns, arrows and arrowhead), increased digit number, and reduced severity of pubis hypoplasia (P columns, arrows). FL, forelimb; P, pelvis; il, ilium; pu, pubis; is, ischium.
(C) Twist1CC pubis defects were scored on a scale of increasing severity from 0 to 4 (left panels) and plotted as a percent fraction of total pelvises scored for each genotype. Reducing Hand2 gene dosage in Twist1CC/CC or Twist1CC/− pelvises significantly shifts pubis scores to lesser values (p<0.001 for each, Mann-Whitney).