Fig. 6. Double-labeling with antisera to either Eps8 or Tbr2 and the α6 subunit of the GABAA receptor with immunofluorescence (panel B) and brightfield microscopy (all other panels) proves that UBCs and granule cells are codistributed within the CN and in neighboring territories. In the brightfield micrographs UBC nuclei are stained red/brown, while the cytoplasm is unstained; by contrast, the cell bodies and glomerular dendrites of granule cells appear as pale blue ringlets with a clear nucleus and deeper blue neuropil areas, respectively.
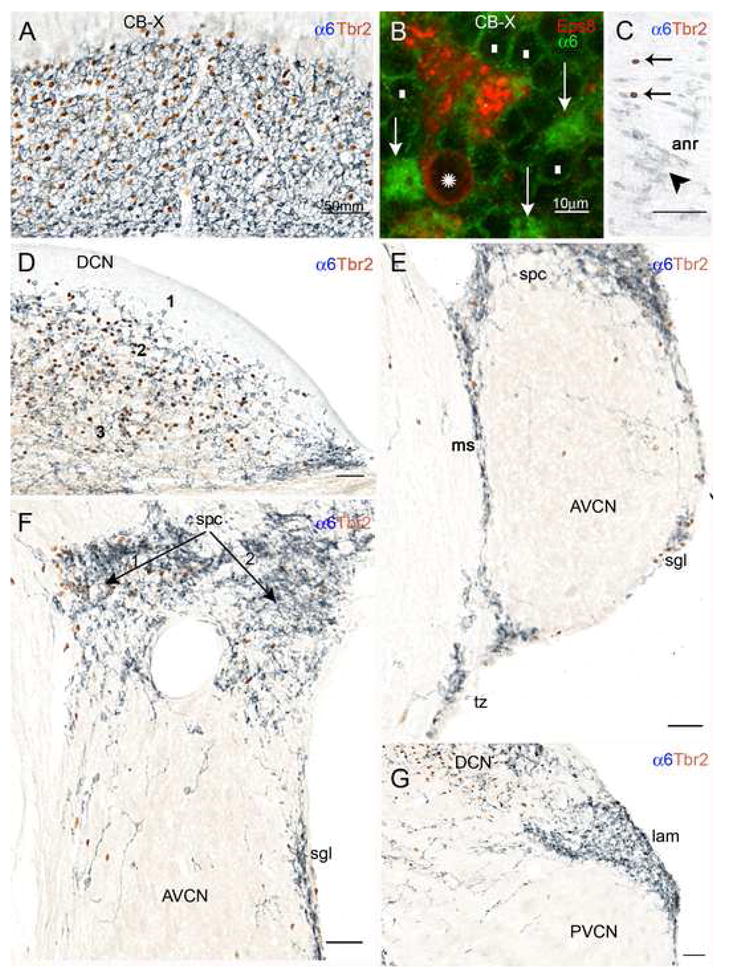
A: Detail from the transition between the cerebellar flocculus and paraflocculus shows high densities of UBC and granule cell immunoreactivities. B: This standard immunofluorescence micrograph shows that the cerebellar UBC (asterisk over the nucleus) labeled by the UBC cell class marker Eps8 lacks α6 immunoreactivity; granule cell bodies (white rectangles) show weak α6 immunoreactivity along the plasma membrane, but their dendritic tips in the glomeruli (arrows) are intensely stained. C: Detail from the cochlear nerve root showing several granule cells (arrowheads) and the nuclei of two UBCs (arrows); D: The DCN contains high densities of UBCs and granule cells in layer 2 and the polymorphic layer 3, but not in the molecular layer 1. E: UBCs and granule cells are present in the medial sheet (ms), superficial granular layer (sgl), and subpeduncular corner (spc), and also in the trapezoid body (tb), and the magnocellular AVCN. F: In the subpeduncular corner the density of granule cells is homogenously high, while UBCs are clustered in the area indicated by arrow 1, and sparse in the area labeled by arrow 2. Scattered granule cells and UBCs are present in the magnocellular AVCN. G: The lamina contains numerous granule cells, but rare UBCs. Scattered granule cells and UBCs are present in the magnocellular PVCN. Magnification bars A, C–G= 50 μm; B= 10 μm.
