Figure 3.
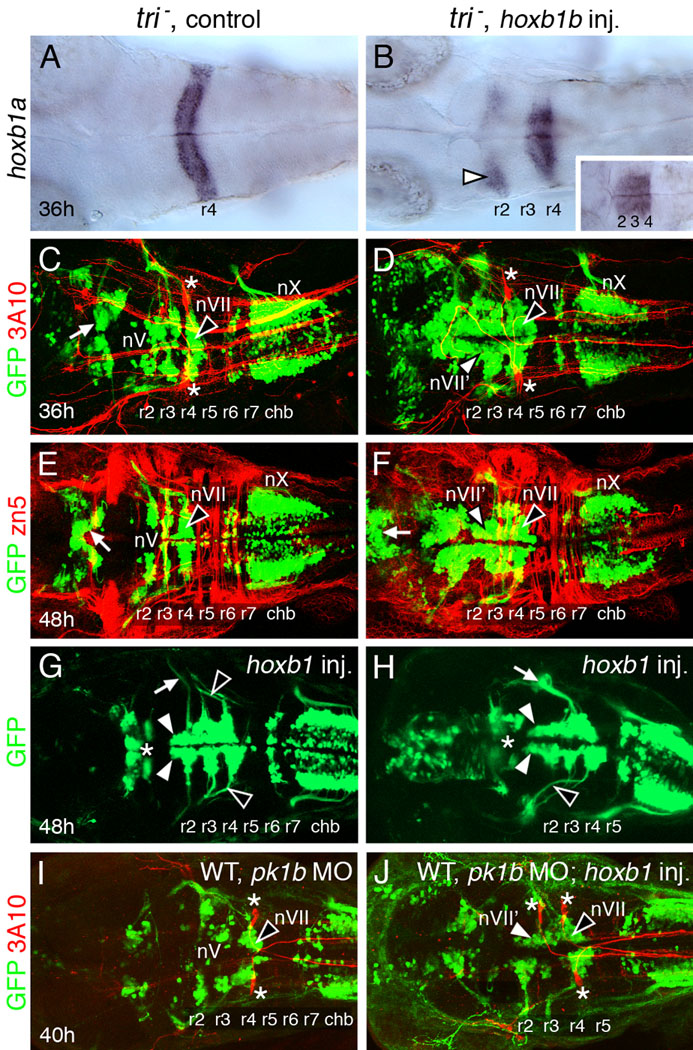
FBMN-like neurons can migrate normally in hoxb1b-injected trilobite mutants and pk1b morphants. All panels show dorsal views of the hindbrain with anterior to the left. Panels C–F, I, J show merged confocal images of GFP-expressing motor neurons (green) and 3A10 antibody-labeled (C, D, I, J) reticulospinal and sensory neurons (red; Mauthner cells in r4 are indicated by asterisks) or zn5 antibody-labeled (E, F) hindbrain commissural neurons and axons (red). (A) In a 36 hpf control tri mutant, hoxb1a is expressed in r4. (B) In a tri mutant injected with hoxb1b RNA, hoxb1a is expressed in r4, but also ectopically in r2 (arrowhead). Hoxb1a expression frequently extends into r3, merging its normal and ectopic expression domains (inset). (C, E) In a 36 hpf control mutant embryo (C), the trigeminal (nV) motor neurons are found in r2 and r3, and the facial branchiomotor neurons (nVII; FBMNs) fail to migrate caudally and remain in r4 (arrowhead). By 48 hpf (E), the nV motor neurons are found in characteristic mediolaterally elongated clusters in r2 and r3, and the FBMNs are still located in r4 (arrowhead). The vagal (nX) motor neurons in the caudal hindbrain (chb) and midbrain motor neurons (arrows) are found in characteristic locations. (D, F) In a 36 hpf hoxb1b-injected tri mutant embryo (D), GFP-expressing motor neurons are found in large numbers in the anterior hindbrain, including r2–r4. The cell bodies form longitudinal columns, suggestive of FBMN-like characteristics (nVII'; white arrowhead). The FBMNs (nVII; black arrowhead) remain in r4 and the vagal (nX) neurons are not affected. In a 48 hpf embryo (F), the medially-positioned longitudinal columns are still evident in r2 and r3 (nVII'; white arrowhead). FBMNs (black arrowhead) remain in r4, while the nX neurons in the caudal hindbrain and the midbrain motor neurons (arrow) are largely unaffected. (G, H) In these 48 hpf hoxb1b-injected tri mutants, motor neuron cell bodies in r2 form longitudinal columns (white arrowheads), suggestive of FBMN-like features. The axons of unaffected nV neurons (white arrow in G) and of FBMNs (black arrowheads) are indicated. For the embryo shown in (H), nV axon fascicles are missing. The nVII fascicle (white arrow) is unusually thick perhaps due to axons of nVII' neurons in r2 and r3 exiting out of r4 with nVII axons. The midbrain motor neurons (asterisks) are only slightly affected in these embryos. (I, J) In a 40 hpf WT embryo injected with pk1b MO (I), the trigeminal (nV) motor neurons are found in r2 and r3, and the facial branchiomotor neurons (nVII; FBMNs) fail to migrate caudally and remain in r4 (arrowhead). In a hoxb1b-injected pk1b morphant (J), GFP-expressing motor neurons in r2 and r3 on one side are located medially in a single elongated cluster that extends up to r4, suggestive of FBMN-like characteristics (nVII'; white arrowhead). The FBMNs (nVII; black arrowhead) remain in r4.
