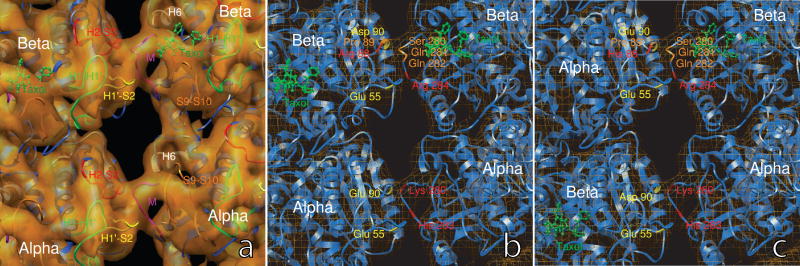
Figure 5.
The structure of inter-PF interactions. (a) The M loop (marked in magenta) of one tubulin molecule interacts with both the H1′-S2 loop (in yellow) and the H2-S3 loop (in red) of the adjacent tubulin molecule in the neighboring PF. The densities of the H1-H1′ loops (in green) merge into the densities of for H1′-S2 loop and the H2-S3, and contribute to stabilizing the H1′-S2 and H2-S3 loops. In the neighboring α-tubulin molecules, the densities from the end of the helix H6 (in white) and the S9-S10 loop (in orange) run into the ring-shaped density of the M loop, and may stabilize the latter. In the β-tubulin molecule, Taxol occupies the pocket between M-loop, S9-S10 loop, H6, and H7, and may push the M loop out to extend further towards the H1′-S2 and H2-S3 loops in the neighboring PF. (b) In the region of perfect helical lattice, the α-α interaction provides an environment of salt bridges between Lys 280 and Glu 90, and between His 283 and Glu 55. The β-β interaction offers an environment conducive for a salt bridge between Arg 284 and Glu 55. The interaction between the M loop and the H2-S3 loop involves segment Ser-Gln-Gln from the M loop and segment Arg-Pro-Asp from the H2-S3 loop.(c) At the seam, the β-α interaction is very similar to that of α-α interaction in the perfect lattice region, and provides a environment for salt bridges Lys 280 - Asp 90 and His 283 - Glu 55. The α-β interaction resembles that of β-β in the perfect lattice region, with salt-bridge-forming residues Arg 284 and Glu 55 very close to one another. The interaction between the M loop and the H2-S3 loop involves segments His-Pro-Glu from the M loop and Ser-Gln-Gln from the H2-S3 loop. The His-Pro-Glu at the seam and the Arg-Pro-Asp in the perfect lattice region are highly conserved and have very similar properties.