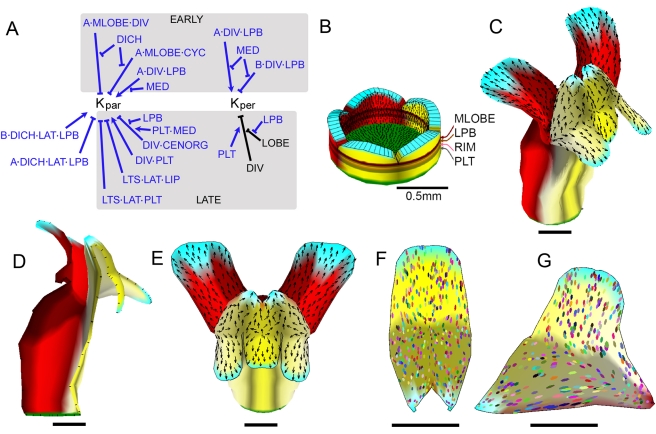
Figure 8. Further modification to the wild-type corolla model.
(A) Part of the KRN (rest as in Figures 6F; 7F) showing modifications to specified growth rates that improve the corolla shape. DICH and LAT with LPB promote Kpar on the B (abaxial) surface and inhibit on the A (adaxial) surface leading to the dorsal petal lobes bending forwards. During the early stage, MLOBE in combination with CYC or DIV (but in the absence of DICH) inhibits Kpar on the A surface, leading to the lobes bending forward. DIV in combination with LPB (but in the absence of MED) promotes Kpar and Kper on the A surface, while inhibiting Kper on the B surface, leading to bulging of the ventral petal junctions. During the late stage, LTS in combination with LAT inhibits Kpar in the lip and palate, preventing excessive growth of lateral boundaries. Growth of the ventral palate is modulated by DIV promoting Kpar in combination with PLT, while DIV in combination with CENORG inhibits Kpar in the absence of LPB and enhanced by PLT and MED, restricting growth of the distal palate. Inhibition of Kper by DIV is promoted by PLT, and by LPB in the LOBE, leading to a narrow ventral palate and lip. For detailed implementation, see Model 6 in Text S1B. (B) Initial (day 10) distribution of additional identity factors used in the model, MLOBE and LPB. (C–E) Mature canvas generated by model based on modifications in (A) shown in oblique view (C), longitudinal section (D), and face view (E). (F–G) Ellipse patterns on computationally flattened ventral (F) and lateral (G) lobes from the mature canvas of the wild-type model incorporating changes in (A) (ellipses originated as circles on day 14). All scale bars are 5 mm unless otherwise indicated.