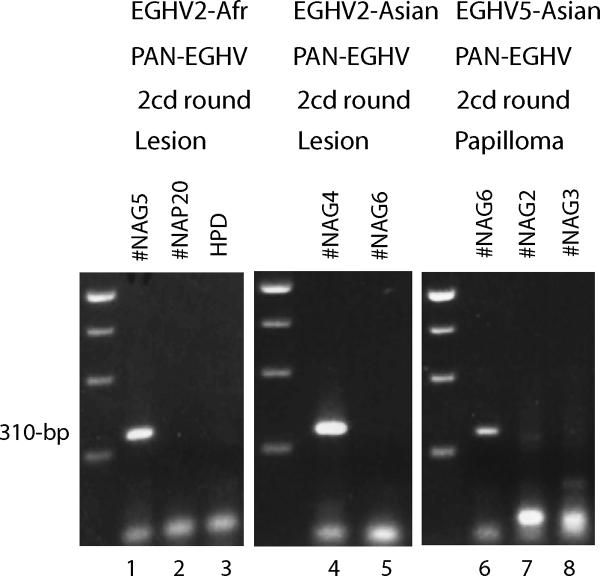
Figure 3. PCR detection of EGHV2 in an African and Asian elephant and EGHV5 in an Asian elephant.
Agarose gel electrophoretic separation of ethidium bromide-stained PCR products obtained using moderately-redundant consensus PAN-EGHV or PAN-EEHV POL primers. Lanes 1 to 5, detection of EGHV2 with first-round PAN-EGHV primers 6784/6788 followed by second-round EGHV2-specific primers 6785/6787 (310-bp). Lanes 1, African elephant #NAG5, vulval lesion; 2, Asian elephant EEHV1-positive case #NAP20; 3, Human placental DNA negative control (HPD); 4, Asian elephant #NAG4, vulval lesion; and 5, Asian elephant #NAG6, trunk papilloma. Lanes 6 to 8, detection of EGHV5 with first-round PAN-EGHV POL primers 6784/6788 followed by second-round PAN-EGHV POL primers 6785/6788 (310-bp); 6, Asian elephant #NAG6, trunk papilloma; 7, Asian elephant #NAG2/4, vulval lesion; and 8, African elephant #NAG3/5, vulval lesion. The three left-hand side lanes contain a 250-bp multimer size marker ladder.