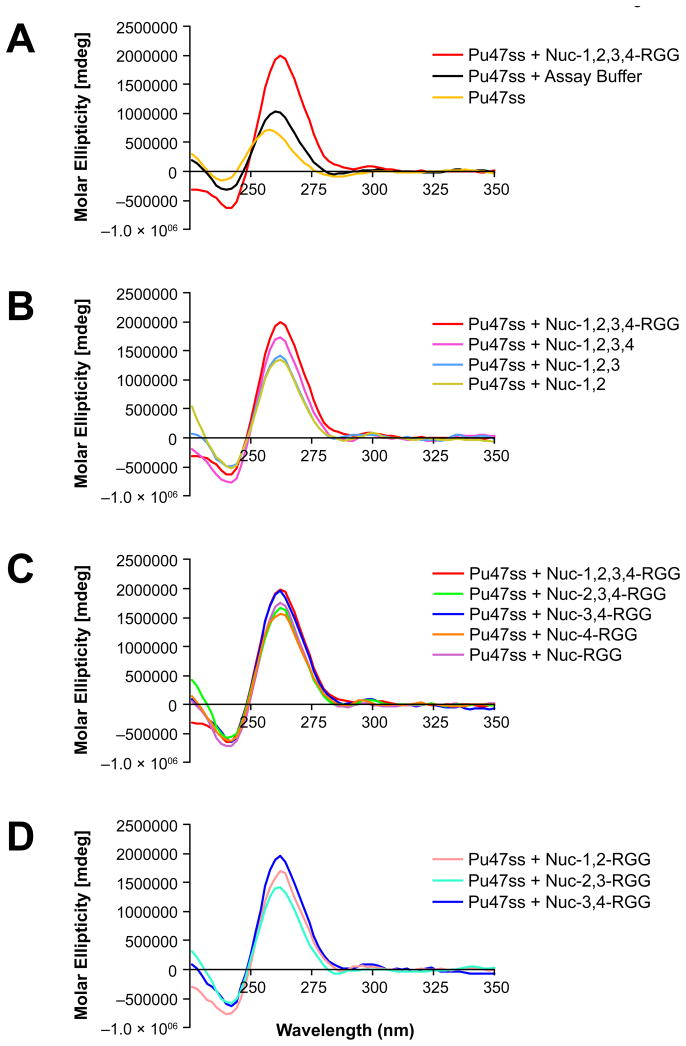
Fig. 3.
Effect of deletion mutagenesis on the ability of nucleolin to induce c-MYC G-quadruplex formation. (A) CD spectra of Pu47ss after incubation with Nuc-1,2,3,4-RGG, or assay buffer containing 20 mM Tris-HCl, pH 7.4, 5 mM NaCl, 1 mM EDTA, in 50% glycerol. (B) CD spectra of Pu47ss after incubation with C-terminal nucleolin deletion mutants. (C) CD spectra of Pu47ss after incubation with nucleolin’s N-terminal deletion mutants. (D) Comparison of the effect of RBD-substitution on the ability of Nuc-3,4-RGG to induce G-quadruplex formation. Formation of a parallel G-quadruplex structure is reflected by the change in wavelength from 258 nm (single-stranded DNA) to 262 nm (G-quadruplex DNA) and increased molar ellipticity at 262 nm.