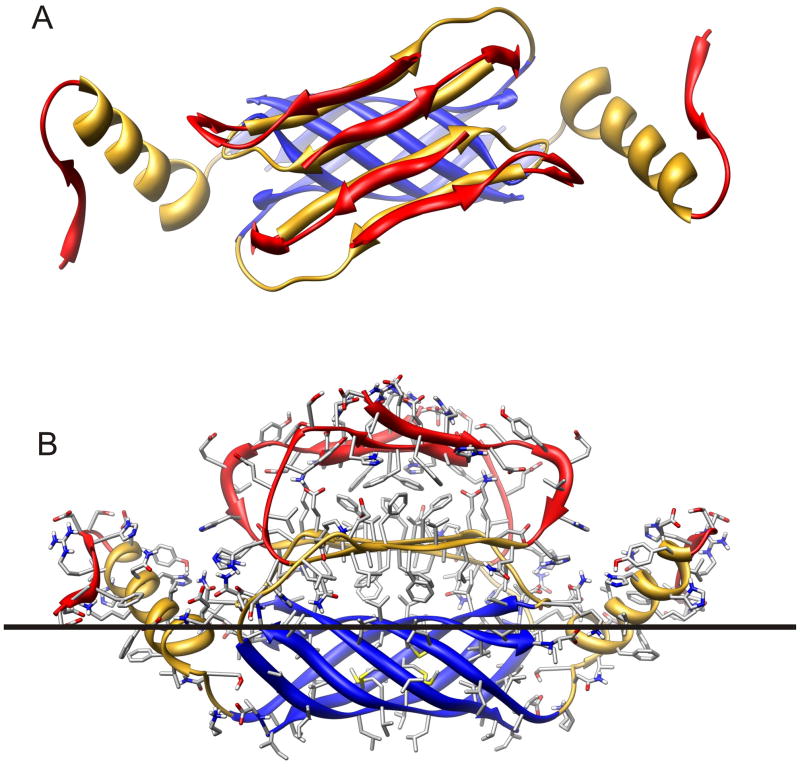
Figure 2.
Ribbon representation of Aβ42 hexamer model bound to the cis surface of the membrane. Segment S1 (residues 1–14) is red, S2 (15–28) is gold, and S3 (29–42) is blue. (A) Hexamer as viewed looking from the aqueous phase toward the membrane. The hexamer has 2-fold symmetry, with three monomeric subunit conformations. The S3 segments from six subunits form a six stranded antiparallel β-barrel with its axis parallel to the membrane surface. S1 and S2 segments of Sub1 and Sub2 comprise two antiparallel β-sheets. The red S1a sheet is on the outer surface were it is exposed to water, the gold S2 sheet is sandwiched between the S1a sheet and S3 β-barrel. S2 of the remaining two Sub3 subunits form α-helices that interact with both water and lipid. The red S1 segment of Sub3 is ill-defined and may have extended and/or coiled conformations. (B) Side view of the hexamer illustrating side chains, colored by element (red = O, blue = N, gray = C, white = H). The black line approximates the boundary between the lipid head group and alkyl chain portions of the membrane. Note that almost all hydrophobic side chains are either buried between sheets, inside the β-barrel, are exposed to lipid alkyl chains and almost all polar and charged groups are exposed to water and/or located where they can form H-bonds and salt bridges.