Table II.
Model Components for the Final Prediction Models
| Parameter | NIHSS | BI |
|---|---|---|
| Linear model for relative improvement | ||
| Constant size of relative score improvement | ■ | ■ |
| Influence of previous score | ▲ | |
| Influence of baseline NIHSS score | ▼ | ▼ |
| Influence of age | ▼ | |
| Variability in linear improvement | ||
| Interindividual variability in relative score change | ||
| Time <14 d | ■ | |
| Time ≥ 14 d | ■ | |
| Linear model for relative decline | ||
| Constant size of relative score decline | ■ | |
| Influence of previous score | ▲ | |
| Influence of time since previous observation | ▼ | |
| Variability in linear decline | ||
| Interindividual variability in relative score change | ■ | |
| Time <14 d | ■ | |
| Time ≥ 14 d | ■ | |
| Residual variability on the logit scale | ■ | ■ |
| Model for probability of improvement | ||
| Baseline probability | ■ | ■ |
| Influence of previous score | ▲ | |
| Influence of age | ▼ | ▼ |
| Model for probability of not reaching maximum score | ||
| Baseline probability | ■ | ■ |
| Influence of previous scorea | ▲ | ▼ |
| Influence of time since previous observation | ▲ | |
| Influence of time since baseline | ▲ | |
| Model for probability of dropoutb | ||
| Baseline probability | ■ | ■ |
| Influence of predicted scorea | ▼ | ▲ |
filled square included, inverted filled triangle produces decline, upright filled triangle produces increase
aA low NIHSS score is positive while a low BI score is negative for the patient, which is the reason for the opposite influence of the previous observation in the two models
bRelationship is proportional, i.e.
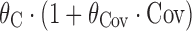 , where θ
C is a baseline term, and θ
Cov is a term describing the effect of covariate or Markovian predictor term Cov
, where θ
C is a baseline term, and θ
Cov is a term describing the effect of covariate or Markovian predictor term Cov
