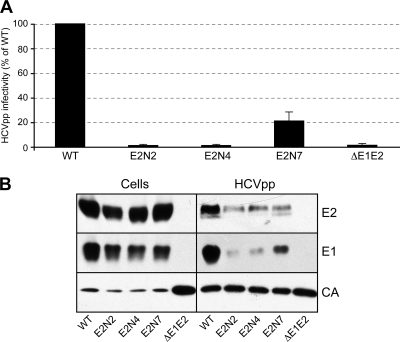
FIG. 4.
Role of glycans E2N2, E2N4, and E2N7 on genotype 2a HCVpp infectivity. (A) Plasmids encoding the E2N2, E2N4, and E2N7 mutants in the context of a genotype 2a (JFH-1) E1/E2 polyprotein were used to generate HCVpp. Infection assays with the luciferase reporter gene were performed by using target Huh-7 cells. Similar inputs of viral particles were used in each experiment, and this was confirmed by comparing the amounts of capsid protein incorporated into HCVpp (see panel B, anti-CA [CA]). Pseudotyped particles produced in the absence of envelope proteins (ΔE1E2) were used as a control. The results are expressed as percentages of wild-type infectivity (WT) and are reported as means ± SDs of three independent experiments. (B) Incorporation of HCV envelope proteins into HCVpp. Particles were pelleted through 20% sucrose cushions and analyzed by Western blotting. HCV envelope glycoproteins and the capsid protein of murine leukemia virus (MLV) were revealed with the following specific MAbs: anti-E1 (A4), anti-E2 (3/11), and anti-CA (R187). Expression of mutant proteins was verified by direct Western blotting of cell lysates.