Figure 2.
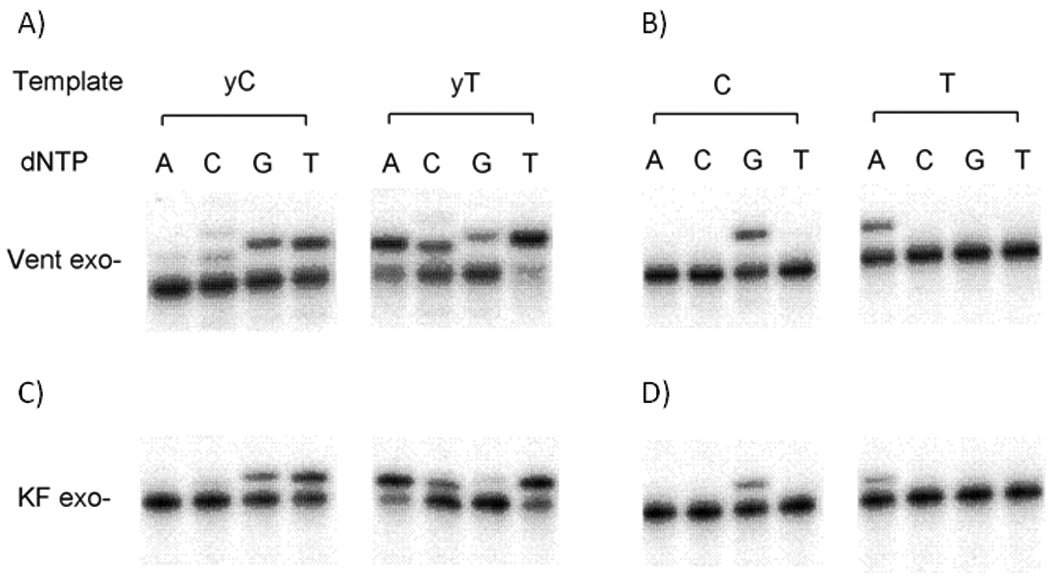
Survey of selectivity of enzymatic nucleotide incorporation opposite yDNA bases. A and C show yDNA template bases; B and D show natural bases as controls. Enzymes are Thermococcus litoralis DNA polymerase (Vent exo−) and Klenow fragment of DNA pol I (KF exo−). Standard 10 µL reactions were performed at 37 °C (KF exo−) or 68 °C (Vent exo−) and contained 25 nM radiolabeled primer-template (primer, 5'-TAA TAC AAC TCA CTA TAG GGA GA-3'; template, 5'-ACT GXT CTC CCT ATA GTG AGT CGT ATT A-3', where X=yT,T,yC, or C). (A) Reaction solution contained 0.4 unit/µL Vent exo−, 500 µM dNTP; reaction time 20 min. (B) Reaction contained 0.05 unit/µL Vent exo−, 50 µM dNTP; reaction time 3 min. (C) Reaction contained 0.02 unit/µL KF exo−, 50 µM dNTP; reaction time 4 min. (D) Reaction containe2 0.005 unit/µL KF exo−,5 µM dNTP; reaction time 3 min. Products were resolved by denaturing polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (7.6 M urea, 20% acrylamide) and visualized by phosphorimaging.
