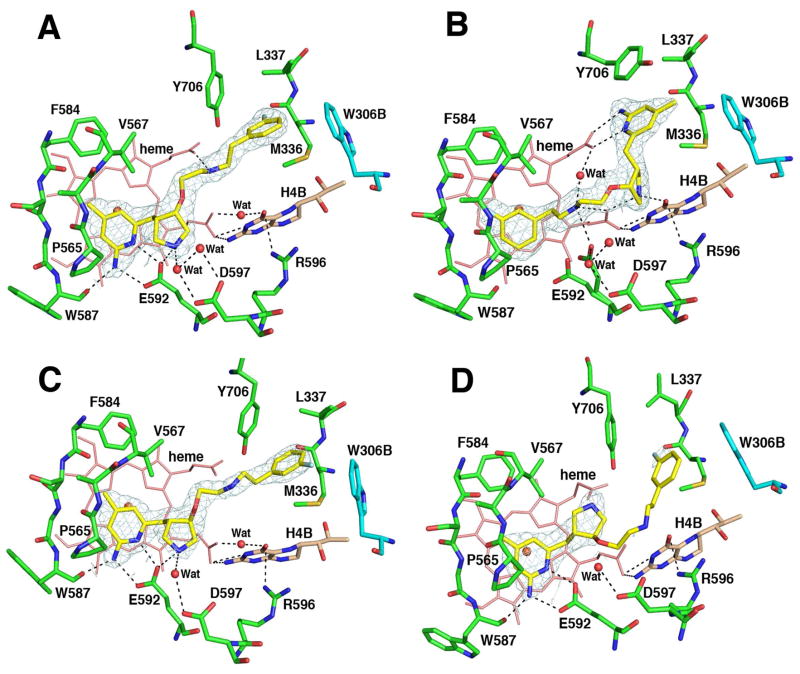
Figure 6.
Crystallographic binding conformations of four enantiomerically pure isomers of 4 [A: (3′S, 4′S)-4, B: (3′R, 4′R)-4, C: (3′R, 4′S)-4, D: (3′S, 4′R)-4] with rat nNOS. Shown also is the 2Fo – Fc electron density for the ligands contoured at 1 σ. The active site residues and ligands are represented in an atom-type style (carbons in green or cyan (chain B), nitrogens in blue, oxygen in red, and sulfur in yellow). The important H-bonds between the residues, structural water, cofactors, and inhibitors are depicted with dashed lines. The resolution and Rwork/Rfree values for the four structures shown are (A) 2.02 Å, 0.183/0.219; (B) 1.85 Å, 0.189/0.222; (C) 2.00 Å, 0.196/0.231; (D) 2.30 Å, 0.201/0.266. The 4-methyl-2-aminopyridine ring in (3′S, 4′S)-4, (3′R, 4′S)-4, and (3′S, 4′R)-4 and the m-fluoro-phenyl ring in (3′R, 4′R)-4 are roughly parallel to the heme plane with the closest distance to the heme iron at 4.0–4.1 Å. It is not clear if this is a π-π stacking interaction or a cation-π interaction.