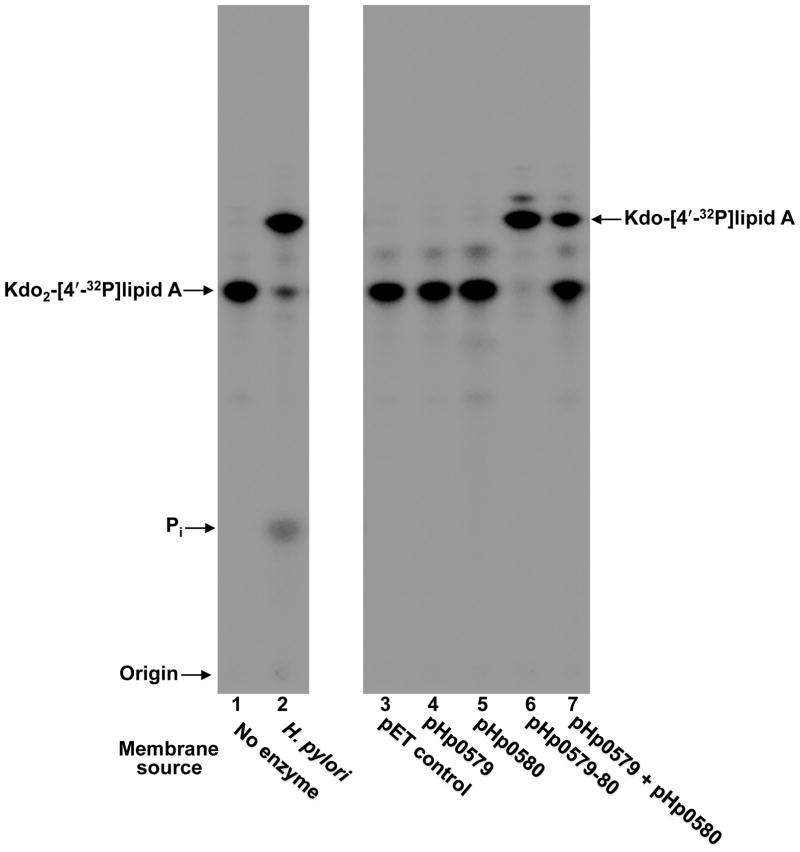
Fig. 2. In vitro assay of Kdo hydrolase candidate proteins, Hp0579 and Hp0580, heterologously expressed in E. coli.
Hp0579, Hp0580 and Hp0579-Hp0580 were overexpresed in E. coli HMS174 and membranes were isolated for use as the enzyme source in an in vitro Kdo-lipid A modification assay, using Kdo2-[4′-32P]lipid A as the substrate. H. pylori membranes isolated from strain Hp7-91 harboring a mutation in hp0021 (1-phosphatase) acted as a positive control and the empty pET21a vector acted as a negative control, demonstrating that E. coli has no endogenous Kdo hydrolase activity. When assayed individually, Hp0579 and Hp0580 were devoid of Kdo hydrolase activity; however, after co-expression a robust Kdo hydrolase activity could be detected by the appearance of a faster migrating product, which co-migrated with the positive control. Mixing membranes from individually expressed Hp0579 and Hp0580 could also generate Kdo hydrolase activity, reinforcing the necessity for a two protein complex. The minor product spots present above both the starting substrate Kdo2-[4′-32P]lipid A and the major product Kdo-[4′-32P]lipid A can be attributed to endogenous E. coli PagP activity, an outer membrane lipid A acyl transferase (Bishop et al., 2000).