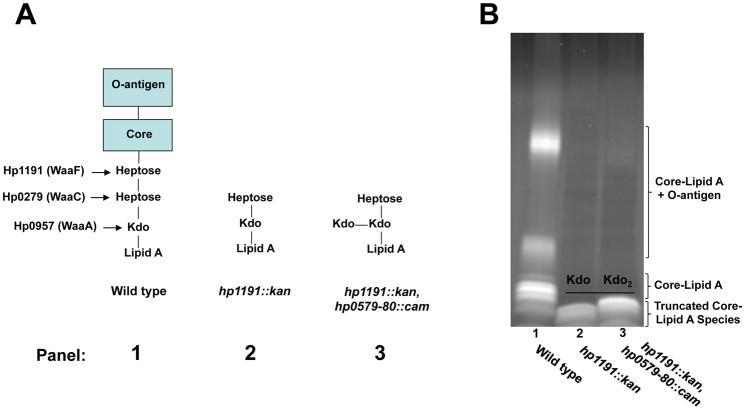
Fig. 4. SDS-PAGE analysis of H. pylori 26695 hp1191::kan and hp1191::kan, hp0579-80::cam LPS profiles.
A. Hp1191 is a heptosyl transferase that is responsible for transferring the second heptose sugar found in the core region of H. pylori 26695 LPS (panel 1). An Hp1191 mutant produces a severely truncated LPS with only two sugars, heptose and Kdo, extending past the lipid A domain (panel 2). The in vitro assays depicted in Figs. 2 and 3 would predict that an hp1191, hp0579-hp0580 mutant would produce an LPS species with 3 sugars extended past the lipid A domain (panel 3). B. The predicted difference in LPS composition, between the hp1191 and hp1191, hp0579-hp0580 mutants was evaluated by SDS-PAGE. As expected the hp1191, hp0579-hp0580 mutant produced a higher mass LPS (lane 3) as compared to the hp1191 mutant (lane 2), demonstrating an in vivo activity for the Kdo hydrolase.